Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 11: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course JEE Advanced solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
- diagram for a process of a given mass of ideal gas is as shown in the figure. During the process, the pressure of the gas
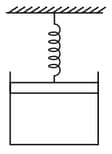
One mole of an ideal gas is kept enclosed under a light piston (area ) connected by a compressed spring (spring constant ). The volume of gas is and its temperature is . The gas is heated so that it compresses the spring further by . The work done by the gas in the process is (Take and suppose there is no atmosphere).
An ideal gas undergoes a thermodynamic cycle as shown in figure.
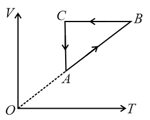
Which of the following graphs may represent the same cycle?
The ratio of r.m.s. speed to the r.ms. angular speed of a diatomic gas at a certain temperature is: (assume mass of one molecule, molecular mass, moment of inertia of the molecules)
Which of the following will have maximum total kinetic energy at temperature .
Initially a gas of diatomic molecules is contained in a cylinder of volume at a pressure and temperature Assuming that of the molecules get dissociated causing a change in number of moles. The pressure of the resulting gas at temperature when contained in a volume is given by The ratio is_____.
A container is divided into two chambers by a partition. The volume of first chamber is litre and second chamber is litre. The first chamber contain moles of gas at pressure atm and second chamber contain moles of gas at pressure atm. After the partition is removed and the mixture attains equilibrium, then, the common equilibrium pressure existing in the mixture is atm. Value of is
At low temperatures, the molar heat capacity of solids at constant pressure depends on the absolute temperature according to the law One mole of solid argon at temperature is brought into thermal contact with of solid argon at a temperature of and they insulated everything together. What will be the temperature (in ) of the substance when thermal equilibrium is established? Round off to nearest integer.
