Reflection and Refraction at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
Important Questions on Reflection and Refraction at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
A concave mirror is placed on a horizontal table, with its axis directed vertically upwards. Let O be the pole of the mirror and C it's centre of curvature. A point object is placed at C. It has a real image, also located at C (a condition called auto-collimation). If the mirror is now filled with water, the image will be:
A ray of light is incident on a glass sphere of refractive index at an angle of incidence as shown in figure. The total deviation (in degree) suffered by the ray is _____ .
A plane mirror and a concave mirror of radius of curvature are placed facing each other, with a point object at the center of them. If the image formed by first reflection at the spherical mirror and then at the plane mirror coincides with the object then the separation (in ) between two mirrors will be _____ .
An object between two parallel (vertical) plane mirrors is approaching plane mirror as shown. If denote the magnitude of relative velocity of image with respect to object in mirror respectively and denotes relative velocity of approach of the images formed due to direct reflection by each mirror, then
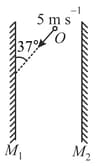
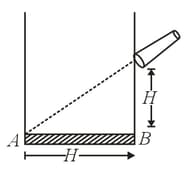
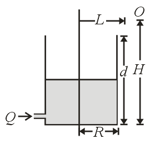
Figure shows a container of width A telescope is fitted at a height above the base on its side wall such that it is focussed at the point as shown. Now aliquid is poured slowly in the container. The refractive index of liquid is Select the correctalternatives
The apparent depth of needle lying at the bottom of the tank which is filled with water to a height of is measured by a microscope to be . If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index to the same height as earlier, then the displacement of the microscope needed to establish the focus on the needle again is . The value of is
A short linear object is placed on the principal axis of convex mirror of focal length as shown in the figure. The ratio of transverse magnification to longitudinal magnification is :
If the refractive indices of water and that of glass with respect to air are and , respectively, then the refractive index of glass with respect to water is,
A small coin is fixed at the center of the base of an empty cylindrical steel container having radius and height . At time , the container starts getting filled with water at a flowrate of without disturbing the coin. Find the approximate time when the coin will first be seen by the observer "" from the height of above and radially away from the coin as shown in the figure. Refractive index of water is .
A prism of refractive index and refracting angle is placed in air. One of the two refracting surfaces of the prism is silvered and a ray of monochromatic light enters the prism from the other face at an angle If the ray retraces its path, then what is the value of (in degree)?
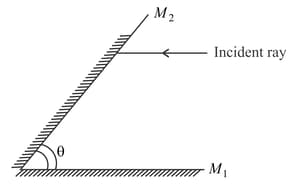
Two plane mirrors and are inclined to each other at an angle . When a ray of light incident on , parallel to (as shown) undergoes a total of eight reflections, it emerges parallel to . Find the value of (in radians). (Approximate the answer to the nearest integer.)
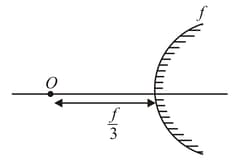
A narrow parallel beam of light falls on a glass sphere of radius and refractive index at normal incidence. The distance of the image from the outer edge is given by:
An object, is placed in front of a convex mirror of focal length . A plane mirror is now placed facing the object in between the object and the convex mirror such that it covers lower half of the convex mirror. What should be the distance of the plane mirror from the object, so that there will be no parallax between the images formed by the two mirrors?
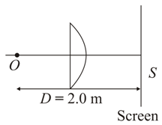
A plano-convex thin lens is used to obtain the image of a point object on the screen as shown in figure. The thickness of the lens in the middle is and refractive index of the material of the lens is If the separation between the object and the screen is to be minimum, then the aperture diameter of the lens (in ) should be (consider lens as thin).
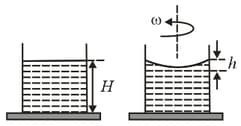
A beaker of radius is filled with water up to a height as shown in the figure on the left. The beaker is kept on a horizontal table rotating with angular speed . This makes the water surface curved so that the difference in the height of water level at the centre and at the circumference of the beaker is , as shown in the figure on the right. Take this surface to be approximately spherical with a radius of curvature Which of the following is/are correct? ( is the acceleration due to gravity)
A compound microscope consists of an objective lens of focal length and an eye piece of focal length with a separation of The distance between an object and the objective lens, at which the strain on the eye is minimum is The value of is.......
An observer can see through a small hole on the side of a jar (radius ) at a point at height of from the bottom. The hole is at a height of . When the jar is filled with a liquid up to a height of the same observer can see the edge at the bottom of the jar. If the refractive index of the liquid is , the value of is:
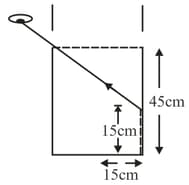
When an object is kept at a distance of from a concave mirror, the image is formed at a distance of from the mirror. If the object is moved with a speed of , the speed (in ) with which image moves at that instant is
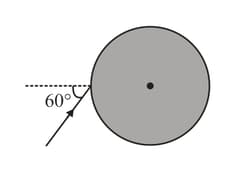
A light ray enters a solid glass sphere of refractive index at an angle of incidence . The ray is both reflected and refracted at the farther surface of the sphere. The angle (in degrees) between the reflected and refracted rays at this surface is:
Critical angle of glass is and that of water is . The critical angle for water and glass surface would be

