Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course COMEDK UGET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
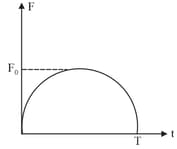
A particle of mass initially at rest, is acted upon by a variable force for a brief interval of time It attains a velocity after the force stops acting. is shown in the graph as a function of time. The curve is a semicircle, find
A bullet of mass is fired from a gun of mass If the bullet moves with the muzzle speed of the impulse imparted to the gun and velocity of recoil of gun are
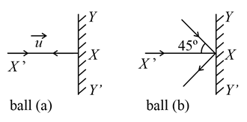
Two billiard balls of equal mass strike a rigid wall with same speed of (as shown) but at different angles. If the balls get reflected with the same speed, then the ratio of the magnitude of impulses imparted to ball and ball by the wall along direction is:
If a shell fired from a canon is exploded in air then-
Sand is being dropped on a conveyor belt at the rate of The force necessary to keep the belt moving with a constant velocity of will be :
For a two particle collision, the following quantities are conserved in general-
A glass ball A of mass moving with a velocity of along -axis hits another ball of mass which is initially at rest (consider the collision as a perfect elastic collision). The velocities of the two balls after collision are
Read the passage and answer the following question:
In all types of collision, the linear momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not conserved in inelastic collision. Two bodies of equal masses interchange their velocities after elastic collision. If after collision, two bodies stick together and move as one body with same velocity, the collision is called inelastic collision.
In elastic collision
