Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Level 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Level 2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Level 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course JEE Main solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Level 2 with Hints & Solutions
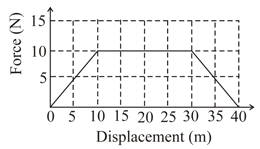
Adjacent figure shows the force-displacement graph of a moving body, the work done in displacing body from to is equal to
A particle with total mechanical energy which is small and negative is under the influence of a one dimensional potential , where is in meters. At time it is at Then at a later time it can be found,
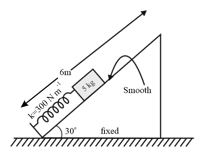
A block of mass is released from rest when compression in spring is . Block is not attached with the spring and natural length of the spring is . Maximum height of block from ground is
A particle of mass moves with speed and collide head on with a stationary particle of mass After the collision, the velocities of the particles are and and is coefficient of restitution for the collision. If is to be positive, i.e. for the first particle to continue moving in same direction then:
During the head-on collision of two masses and the maximum energy of deformation is If before the collision the masses are moving in the same direction, then their velocity of the approach before the collision is
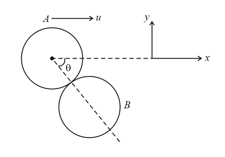
In the figure shown, coefficient of restitution between and is then
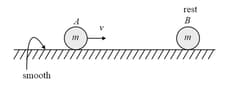
A ball of mass collides elastically with another identical ball at rest as shown in the figure. Initially, velocity of the ball is After collision
In the figure given below, the mass on the left is moving to the right with a constant velocity and after colliding inelastically with the mass on the right, sticks to it. If the spring of spring constant was initially at its equilibrium position, what is the amplitude to the resultant oscillation?