Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory, Exercise 1: Level 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory, Exercise 1: Level 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory, Exercise 1: Level 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course NEET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory, Exercise 1: Level 1 with Hints & Solutions
Consider a sample of oxygen behaving like an ideal gas. At , the ratio of root-mean-square (RMS) velocity to the average velocity of the gas molecule would be :
(Molecular weight of oxygen is )
Assertion: An ideal gas is enclosed within a container fitted with a piston. When volume of this enclosed gas is increased at constant temperature, the pressure exerted by the gas on the piston decreases.
Reason: In the above situation, the rate of molecules striking the piston decreases. If the rate ạt which molecules of a gas having same average speed striking a given area of the wall decreases, the pressure exerted by gas on the wall decreases.
The volume of an enclosure contains a mixture of three gases, of oxygen, of nitrogen and of carbon dioxide at absolute temperature . Consider as universal gas constant. The pressure of the mixture of gases is :
One of a diatomic gas is at pressure of . The density of the gas is . What is the energy of the gas due to thermal motions?
A mixture of moles of helium gas (atomic mass) and mole of argon gas (atomic mass) is kept at in a container. The ratio of the rms speed is
A gas mixture consists of moles of oxygen and moles of argon at temperature . Neglecting all vibrational modes, the total internal energy of the system is
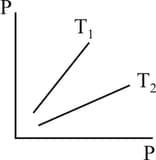
Figure shows graphs of pressure vs density for an ideal gas at two temperatures and
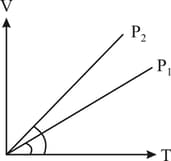
In the following diagram what is the relation between and