Young's Modulus(Y): Elasticity in Length
Important Questions on Young's Modulus(Y): Elasticity in Length
A sphere of radius and mass is attached to the lower end of a steel wire of length and diameter The wire is suspended from high ceiling of a room. When the sphere is made to swing as a simple pendulum, it just grazes the floor at its lowest point. Young's modulus of steel is Find the velocity of the sphere at the lowest position in (Given: )
(Take )
Two steel wires of same length but radii and are connected together end to end and tied to a wall as shown.

The force stretches the combination by How far does the midpoint $A$ move (in )?
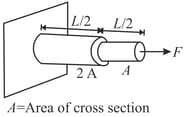
The bar shown in the figure is made of a single piece of material. It is fixed at one end. It consists of two segments of equal length each but different cross-sectional area $A$ and Find the ratio of total elongation in the bar to the elongation produced in thicker segment under the action of an axial force Consider the shape of joint to remain circular. (Given: is Young's modulus).
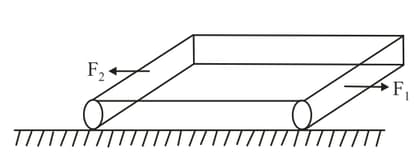
Two opposite forces and act on an elastic plank of modulus of elasticity and length placed over a smooth horizontal surface. The cross-sectional area of the plank is The change in length of the plank is Find the value of
A light rod of length is suspended from the ceiling horizontally by means of two vertical wires of equal length tied to its ends. One of the wires is made of steel and is of cross section . The other wire is a brass of cross section A weight is suspended from a certain point of the rod such that equal stress are produced in both the wires. Which of the following are correct?
A uniform elastic rod of cross-section area , natural length and Young's modulus is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. Now two horizontal forces (of magnitude and ) directed along the length of rod and in opposite direction act at two of its ends as shown. After the rod has acquired steady state, the extension of the rod will be

A rod of square cross section on a side and long is pulled along a smooth horizontal surface by a force applied at one end. The rod has a constant acceleration of Determine the elongation in the rod. (Young's modulus of the material of the rod is ).
The length of a steel cylinder is kept constant by applying pressure at its two ends. When the temperature of rod is increased by from its initial temperature, the increase in pressure to be applied at its ends is
Two bars and of circular cross section, same volume and made of the same material, are subjected to tension. If the diameter of is half that of and if the force applied to both the rod is the same and it is in the elastic limit, the ratio of extension of to that of will be
A wire is suspended vertically from a rigid support. When loaded with a steel weight in air, the wire extends by . When the weight is completely immersed in water, the extension is reduced to . The relative density of the material of the weight is
Two wires of the same material and same mass are stretched by the same force. Their lengths are in the ratio . Their elongations are in the ratio
A wire of length and radius is fixed at one end. When a stretching force is applied at free end, the elongation in the wire is . When another wire of same material but of length and radius , also fixed at one end is stretched by a force applied at free end, then elongation in the second wire will be
A wire of cross section is stretched horizontally between two clamps located apart. A weight is suspended from the mid-point of the wire. If the mid-point sags vertically through a distance the strain produced is . If the Young's modulus of the material is , the value of extension is
Two identical wires of iron and copper with their Young's modulus in the ratio are suspended at same level. They are to be loaded so as to have the same extension and hence level. Ratio of the weight is
A piece of copper wire has twice the radius of a piece of steel wire. Young's modulus for steel is twice that of the copper. One end of the copper wire is joined to one end of the steel wire so that both can be subjected to the same longitudinal force. By what fraction of its length will the steel have stretched when the length of the copper has increased by ?
Two wires of the same material have lengths in the ratio and their radii are in the ratio . If they are stretched by applying equal forces, the increase in their lengths will be in the ratio
When a weight of is suspended from a copper wire of length and diameter , the length of the wire increases by . If the diameter is doubled, the extension produced is
Two wires of the same material and length are stretched by the same force. Their masses are in the ratio . Their elongations are in the ratio
The dimensions of four wires of the same material are given below. In which wire the increase in the length will be maximum?
On applying a stress of , the length of wire of some material gets doubled. Value of Young's modulus for the material of wire in , is (assume Hooke's law to be valid and go for approx. results)

