David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Forces: Vectors and Moments, Exercise 2: Questions
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Forces: Vectors and Moments, Exercise 2: Questions
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Forces: Vectors and Moments, Exercise 2: Questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook 3rd Edition Digital Access solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Forces: Vectors and Moments, Exercise 2: Questions with Hints & Solutions
A parachutist weighs . When she opens her parachute, it pulls upwards on her with a force of
Draw a diagram to show the forces acting on the parachutist.
A parachutist weighs . When she opens her parachute, it pulls upwards on her with a force of
Calculate the resultant force acting on her.
A parachutist weighs . When she opens her parachute, it pulls upwards on her with a force of
What effect will this force have on her?
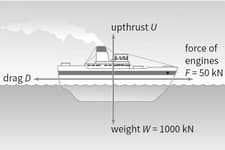
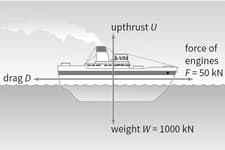
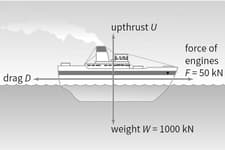
The ship shown in Figure is travelling at a constant velocity.
Is the ship in equilibrium (in other words, is the resultant force on the ship equal to zero)? How do you know?
The force is the frictional drag of the water on the boat. Like air resistance, drag is always in the opposite direction to the object's motion.
The ship shown in Figure is travelling at a constant velocity.
What is the upthrust Of the water?
The force Is the frictional drag of the water on the boat. Like air resistance, drag is always in the opposite direction to the object's motion.
The ship shown in Figure is travelling at a constant velocity.
What is the drag of the water?
The force is the frictional drag of the water on the boat. Like air resistance, drag is always in the opposite direction to the object's motion.
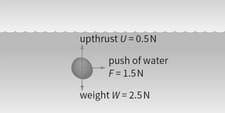
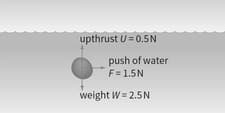
A stone is dropped into a fast-flowing stream. It does not fall vertically because of the sideways push of the water. Calculate the resultant force on the stone.
A stone is dropped into a fast-flowing stream. It does not fall vertically because of the sideways push of the water
Is the stone in equilibrium?