David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Quantum Physics, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Quantum Physics, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 28: Quantum Physics, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook 3rd Edition Digital Access solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Quantum Physics, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
The diagram shows the principles of an electron tube used to demonstrate electron diffraction.
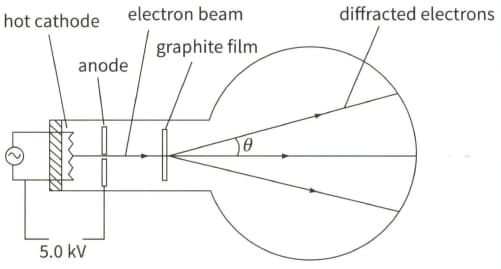
Calculate the kinetic energy $E$ (in joules) of the electrons incident on the graphite film.
The diagram shows the principles of an electron tube used to demonstrate electron diffraction.
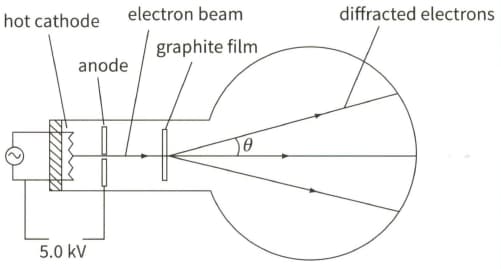
Show that the momentum of an electron is equal to $\sqrt{2 E m_{e}}$ where $m_{\mathrm{e}}$ is the mass of an electron, and hence calculate the momentum of an electron. $\left(m_{\mathrm{e}}=9.11 \times 10^{-31} \mathrm{~kg}\right)$
The diagram shows the principles of an electron tube used to demonstrate electron diffraction.
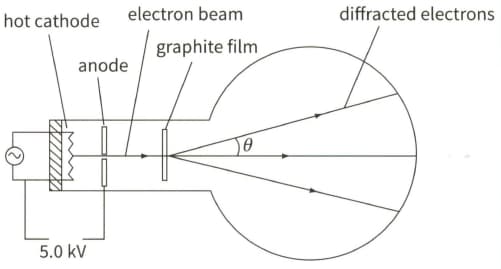
Calculate the de Broglie wavelength of the electrons.
Explain how the wavelengths of neutrons and electrons moving with the same energy would compare.
Describe the importance of the Planck constant in describing the behaviour of electromagnetic radiation and of electrons.
Light of wavelength is incident normally on a metal plate. The intensity of the light is . All the incident light is absorbed by the metal plate. The plate has dimensions .
Explain how the light hitting the plate exerts force on the plate.
(b) Light of wavelength is incident normally on a metal plate. The intensity of the light is . All the incident light is absorbed by the metal plate. The plate has dimensions . Calculate the momentum of each photon of light. (Use: )
(b) Light of wavelength is incident normally on a metal plate. The intensity of the light is . All the incident light is absorbed by the metal plate. The plate has dimensions . Calculate the force exerted on the plate due to the light.
