David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Thermal Physics, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
David Sang Physics Solutions for Exercise - David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Thermal Physics, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 19: Thermal Physics, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook 3rd Edition Digital Access solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from David Sang and Graham Jones Solutions for Chapter: Thermal Physics, Exercise 11: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
What is the internal energy of an object?
The change in mass of the nitrogen is measured over a specific time interval with the heater switched off. The heater is switched on, transferring energy at , and the change of mass is found once more. The results are shown in the table
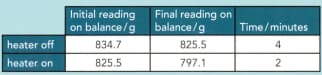
Calculate the specific latent heat of vaporisation of liquid nitrogen.
Explain what is meant by internal energy
Explain what is meant by the absolute zero of temperature.
An electric hot water heater has a power rating of The water is heated as it passes through the heater. Water flows through the heater at a speed of through pipes that have a total cross-sectional area of The temperature of the water entering the heater is
Calculate the mass of water flowing through the heater each second
An electric hot water heater has a power rating of The water is heated as it passes through the heater. Water flows through the heater at a speed of through pipes that have a total cross-sectional area of The temperature of the water entering the heater is
Calculate the temperature at which the water leaves the heater.
An electric hot water heater has a power rating of The water is heated as it passes through the heater. Water flows through the heater at a speed of through pipes that have a total cross-sectional area of The temperature of the water entering the heater is
State any assumptions you have to made in the calculation of mass of water flowing through the heater each second and temperature at which the water leaves the heater.
An electric hot water heater has a power rating of The water is heated as it passes through the heater. Water flows through the heater at a speed of through pipes that have a total cross-sectional area of The temperature of the water entering the heater is
It is possible to adjust the temperature of the water from the heater. Suggest how the temperature of the water could be increased without increasing the power of the heater. (Density of water= specific heat capacity of water )
