Interference
Important Questions on Interference
The graph shows the intensity pattern from a two-slits interference experiment.
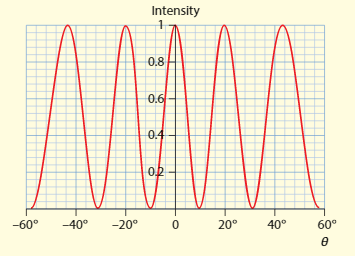
b. Suggest how the pattern in the previous question change if the slit separation changes.
The graph shows the intensity pattern from a two-slits interference experiment.
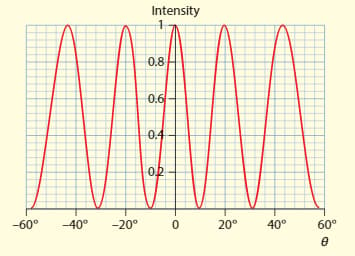
a. Determine the separation of the slits in terms of the wavelength of light used.
Light is incident normally on two narrow parallel slits a distance of apart. A screen is placed a distance of from the slits. The distance on the screen between the central maximum and the centre of the bright spot is measured to be .
b. This experiment is repeated in water (of refractive index ). Suggest how the distance of would change, if at all.
Light is incident normally on two narrow parallel slits a distance of apart. A screen is placed a distance of from the slits. The distance on the screen between the central maximum and the centre of the bright spot is measured to be .
a. Determine the wavelength of light.
In a Young's two-slit experiment it is found that an -order maximum for a wavelength of coincides with the maximum of light of wavelength . Determine .
A thin soap bubble of the index of refraction is viewed with the light of wavelength and appears very bright. Predict a possible value of the thickness of the soap bubbles.
A piece of glass of index of refraction is coated with a thin layer of magnesium fluoride of the index of refraction . It is illuminated with light of the wavelength of . Determine the minimum thickness of the coating that will result in no reflection.
Describe how the graph you drew in a change when:
ii The number of slits stays at two but their separation decreases.
Describe how the graph you drew in a change when:
i. The number of slits increases but their separation stays the same.
Draw a graph to show the variation with angle of the intensity of light observed on a screen some distance from two very narrow, parallel slits when coherent monochromatic light falls on the slits.
Two very narrow, parallel slits separated by a distance of are illuminated by coherent, monochromatic light of wavelength .
c. By drawing another graph on the same axes, illustrate the effect on the intensity distribution of increasing the width of the slits to .
Two very narrow, parallel slits separated by a distance of are illuminated by coherent, monochromatic light of wavelength .
b. Draw a graph to show the intensity of light observed on a screen far from the slits.
Two very narrow, parallel slits separated by a distance of are illuminated by coherent, monochromatic light of wavelength .
a. Describe what is meant by coherent and monochromatic light.
A grating with is illuminating with the light of wavelength .
b. Determine the largest order that can be seen with which this grating and this wavelength.
A grating with is illuminating with the light of wavelength .
a. Determine the angles at which maxima are observed.
Explain why two identical flashlight pointing light to the same spot on a screen will never produce an interference pattern.
In Young's two-slit experiment, a coherent source of light of wavelength is used to illuminate two very narrow slits a distance of apart. A screen is placed at a distance of from the slits. Calculate the separation of two successive bright spots.
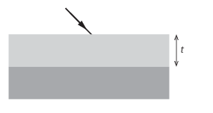
Monochromatic light of wavelength in air is incident on a rectangular piece of glass of refractive index 1.60 that is coated by a thin layer of magnesium fluoride of refractive index 1.38.

Copy and complete this diagram by drawing the paths of the two rays, originating with the incident ray, that will interfere in the eye of an observer looking down on the glass from above.
Light is incident on very thin parallel slits and an interference pattern is formed on a screen a distance away. The number of slits is increased while the separation of two consecutive slits stays the same. Which is correct as N increases?
A light is incident essentially normally on a thin film of thickness and refractive index , The film is on a transparent glass of refractive index . Which of the following condition of the wavelength in oil leads to the destructive interference of the reflective light