Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics & Thermochemistry, Exercise 2: KVPY PROBLEMS (PREVIOUS YEARS)
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics & Thermochemistry, Exercise 2: KVPY PROBLEMS (PREVIOUS YEARS)
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 5: Thermodynamics & Thermochemistry, Exercise 2: KVPY PROBLEMS (PREVIOUS YEARS) with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Practice Book for KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SA Chemistry solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics & Thermochemistry, Exercise 2: KVPY PROBLEMS (PREVIOUS YEARS) with Hints & Solutions
The molar enthalpy change for at and is . Assuming ideal behaviour, the internal energy change for vaporisation of of water at and in is:
Given that the bond energies of: is is is , and is , the heat of formation of hydrazine in the gas phase in is:
The standard free energy change (in ) for the reaction given and is .
For the reaction where (the average bond energies are and ). The heats of the formation of and in , respectively, are closest to:
Given:
The enthalpy change for the following reaction is:
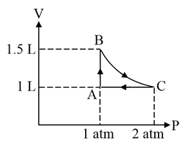
A system consisting of of an ideal gas undergoes a reversible process, (schematically indicated in the figure below). If the temperature at the starting point is and the work done in the process is , the heat exchanged in the entire process in is:
Nitroglycerin (Molecular weight ) detonates according to the following equation:
The standard molar enthalpies of formation, , for the compounds are given below:
.
.
The enthalpy change when nitroglycerine is detonated is:
The quantity of heat (in ) required to raise the temperature of of ethanol from to the boiling point and then change the liquid to vapor at that temperature is closest to [Given: Boiling point of ethanol ]
Specific heat capacity of liquid ethanol .
Latent heat of vaporization of ethanol ].
