Addressing Modes
Important Questions on Addressing Modes
Which is the most appropriate match for the items in the first column with the items in the second column?
X. Indirect Addressing.
Y. Indexed Addressing.
Z. Base Register Addressing.
I. Array implementation
II. Writing Relocatable code
III. Passing array as parameter
The following are some of the sequences of operations in the instruction cycle, which one is the correct sequence?
Match the following
| List I | List II |
| A. Base addressing | (p) Reentrancy |
| B. Indexed addressing | (q) Accumulator |
| C. Stack addressing | (r) Array |
| D. Implied addressing | (s) position independent |
RISC processor have _____.
To which pin on the RAM chip does the address decoder connect in order to sign 1 which memory chip is being accessed?
The most relevant addressing mode to write position independent codes is _____.
The index register in a digital computer is used for?
In which addressing mode, the address of the location of the operand is given explicitly as a part of the instruction?
Adding a constant value to the contents of register?
Which of the following addressing modes, facilitates access to an operand whose location is defined relative to the beginning of the data structure in which it appears?
n this addressing mode, the operand is given explicitly in the instruction.
In which addressing mode the contents of a register specified in the instruction are first decremented, and then these contents are used as the effective address of the operands.
The most relevant addressing mode to write position independent code is_____.
A collection of lines that connects several devices is called _____.
In which addressing mode the effective address of the operand is the contents of a register specified in the instruction and after accessing the operand, the contents of this register is incremented to point to the next item in the list?
In immediate addressing the operand is placed _____
Computers use addressing mode techniques for _____.
In a general-purpose computer system, the CPU, the main memory and the cache may be interconnected via one or more shared system bus(es). However, input/output devices (eg. Hard disk, network interfaces) may only be connected to the system bus through an I/O controller. The following are four statements regarding the requirement for an I/O controller.
1. The capacities of I/O devices are magnitude order larger than that of main memory and hence direct interfacing is impossible.
2. The response times of I/O devices are magnitude order slower than that of CPU and hence direct interfacing is impossible.
3. It is always better to offload the I/O processing to a secondary processor on the I/O controller board than to depend on the primary CPU for I/O processing.
4. The variety of I/O devices in the market requires that a separate I/O controller exists for each device.
What statement(s) best explain the requirement for an I/O controller?
The following diagram shows, which addressing mode?
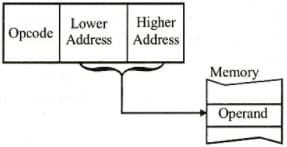
In which addressing mode, the effective address of the operand in generated by adding a constant value to the contents of a register?

