R P Goyal and S P Tripathi Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 7: EXERCISE-2(D)
R P Goyal Physics Solutions for Exercise - R P Goyal and S P Tripathi Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 7: EXERCISE-2(D)
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 7: EXERCISE-2(D) with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Selina Icse Concise Physics For Class 10 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from R P Goyal and S P Tripathi Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 7: EXERCISE-2(D) with Hints & Solutions
Show that the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy (i.e., total mechanical energy) is always conserves in the case of a freely falling body under gravity (with air resistance neglected) from a height h by finding it when (i) the body is at the top, (ii) the body has fallen a distance x, (iii) the body has reached the ground.
A pendulum is oscillating on either side of its rest position. Explain the energy changes that take place in the oscillating pendulum. How does mechanical energy remain constant in it ? Draw the necessary diagram.
A pendulum with bob of mass m is oscillating on either side from its resting position A between the extremes B and C at a vertical height h and A. what is the kinetic energy K and potential energy U when the pendulum is at position (i) A, (ii) B and (iii) C?
A ball of mass is thrown vertically up with an initial velocity so as to reach a height . The correct statement is:
A metal ball of mass is allowed to fall freely from rest from a height of above the ground. What happens to the mechanical energy after the ball hits the ground and comes to rest? (Given, )
The diagram given below shows a ski jump. A skier weighing stands at at the top of the ski jump. He moves from to and takes off for his jump at .
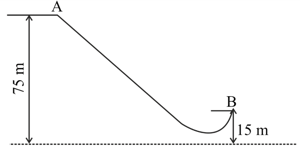
If of the energy in part (a) becomes kinetic energy at . Calculate the speed at which the skier arrives at .(Take )
A hydroelectric power station takes its water from a lake whose water level is at a height of above the turbine. Assuming an overall efficiency of , calculate the mass of water which must flow through the turbine each second to produce power output of . (Take )
The bob of a simple pendulum is imparted a velocity of when it is at its mean position. To what maximum vertical height will it rise on reaching at its extreme position if of its energy is lost in overcoming the friction of air? (Take )
