Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Electric Potential, Exercise 1: Problems
Resnick & Halliday Physics Solutions for Exercise - Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Electric Potential, Exercise 1: Problems
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 24: Electric Potential, Exercise 1: Problems with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Principles Of Physics International Student Version solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Electric Potential, Exercise 1: Problems with Hints & Solutions
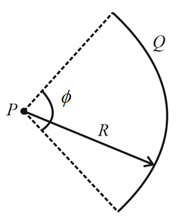
In the figure, a plastic rod which has a uniformly distributed charge has been bent into a circular arc of a radius and the central angle . With at infinity, what is the electric potential at , the centre of curvature of the rod?
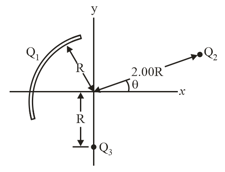
In the given figure, what is the net electric potential at the origin due to the circular arc of charge , the two particles of charges and ? The arc's centre of curvature is at the origin and its radius is , the angle indicated is . What is the net electric potential at the origin if both and are doubled?
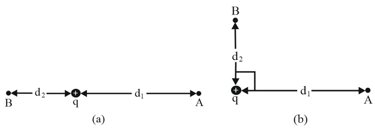
Consider a particle with charge , point at distance from and the point at distance . If and are diametrically opposite to each other as in the figure, (a) what is the electric potential difference ? (b) what is the electric potential difference if and are located as in the figure (b)?
The electric potential at points in an plane is given by, . What are,
(a) the magnitude and (b) the angle (relative to ) of the electric field at the point ?
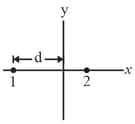
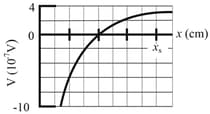
Two charged particles are shown in figure. (a) Particle , with charge , is fixed in place at distance . Particle , with charge , can be moved along the -axis. Figure (b) gives the net electric potential at the origin due to the two particles as a function of the -co-ordinate of particle . The scale of the -axis is set by, . The plot has an asymptote of as . What is in terms of ?
An infinite non-conducting sheet has a surface charge density, .
(a) How much work is done by the electric field due to the sheet if a particle of charge, is moved from the sheet to a point at distance, from the sheet?
(b) If the electric potential is defined to be on the sheet, what is at ?
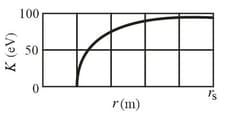
Figure (a) shows an electron moving along the electric dipole axis towards the negative side of the dipole. The dipole is fixed in place. The electron was initially very far from the dipole with kinetic energy . Figure (b) gives the kinetic energy of the electron versus its distance from the dipole centre. The scale of the horizontal axis is set by, . What is the magnitude of the dipole moment?

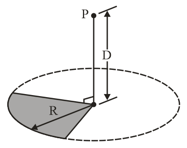
A plastic disk of radius, is charged on one side with a uniform surface charge density , and then three quadrants of the disk are removed. The remaining quadrant is shown in the figure with at infinity, what is the potential due to the remaining quadrant at point , which is on the central axis of the original disk at distance from the original centre?