Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Force and Motion-II, Exercise 1: Problems
Resnick & Halliday Physics Solutions for Exercise - Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Force and Motion-II, Exercise 1: Problems
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 6: Force and Motion-II, Exercise 1: Problems with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Principles Of Physics International Student Version solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Force and Motion-II, Exercise 1: Problems with Hints & Solutions
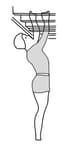
In about , Henry Sincosky of Philadelphia suspended himself from a rafter by gripping the rafter with the thumb of each hand on one side and the fingers on the opposite side (In the figure shown below). Sincosky's mass was . If the coefficient of static friction between hand and rafter was , what was the least magnitude of the normal force on the rafter from each thumb or opposite fingers? (After suspending himself, Sincosky chinned himself on the rafter and then moved hand-over-hand along the rafter. If you do not think Sincosky's grip was remarkable, try to repeat his stunt.)
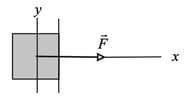
A worker pushes horizontally on a crate with a force of magnitude . The coefficient of static friction between the crate and the floor is .
(a) What is the value of under the circumstances?
(b) Does the crate move?
(c) What is the frictional force on the crate from the floor?
(d) Suppose, next, that a second worker pulls directly upward on the crate to help out. What is the least vertical pull that will allow the first worker's push to move the crate?
(e) If, instead, the second worker pulls horizontally to help out, what is the least pull that will get the crate moving?
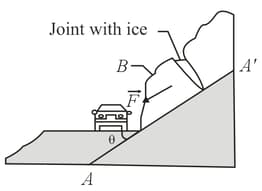
In the figure shown below, the cross section of a road cut into the side of a mountain. The solid line represents a weak bedding plane along which the sliding is possible. Block directly above the highway is separated from uphill rock by a large crack (called a joint), so that only friction between the block and the bedding plane prevents sliding. The mass of the block is , the dip angle of the bedding plane is and the coefficient of static friction between the block and plane is . (a) Show that the block will not slide under these circumstances.
(b) Next, water seeps into the joint and expands upon freezing, exerting on the block a force parallel to . What minimum value of force magnitude will trigger a slide down the plane?
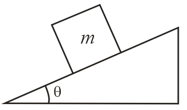
In the figure shown below, a block of mass is at rest on a ramp. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the ramp is not known. Find the magnitude of the net force exerted by the ramp on the block.
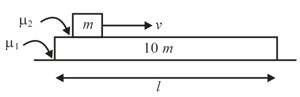
In the figure shown below a small block of mass is sent sliding with velocity along a slab of mass, starting at a distance of from the far end of the slab. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the slab and the floor is that between the block and the slab is with . (a) Find the minimum value of such that the block reaches the far end of the slab. (b) For that value of , how long does the block take to reach the far end?
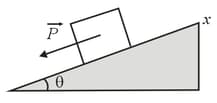
In the figure shown below a force acts on a block weighing . The block is initially at rest on a plane inclined at angle to the horizontal. The positive direction of the -axis is up the plane. Between block and plane, the coefficient of static friction is and the coefficient of kinetic friction is . In unit-vector notation, what is the frictional force on the block from the plane when is (a) (b) and (c)?
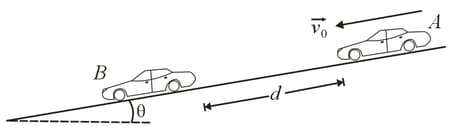
You testify as an expert witness in a case involving an accident in which car slid into the rear of car , which was stopped at a red light along a road headed down a hill (shown in the figure below). You find that the slope of the hill is . The cars were separated by distance when the driver of car put the car into a slide (it lacked any automatic anti-lock braking system). The speed of car at the onset of braking was . With what speed did car hit car , if the coefficient of the kinetic friction was
(a) (dry road surface)?
(b) (road surface covered with wet leaves)?
A horizontal force pushes a block weighing against a vertical wall (In the figure shown below). The coefficient of static friction between the wall and the block is , and the coefficient of kinetic friction is . Assume that the block is not moving initially. (a) Will the block move? (b) In unit-vector notation, what is the force on the block from the wall?