Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Problems
Resnick & Halliday Physics Solutions for Exercise - Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Problems
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 18: Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Problems with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Principles Of Physics International Student Version solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Problems with Hints & Solutions
A ice cube at its melting point is added to of tea (water) initially at in a well-insulated container. When equilibrium is reached, what has been the decrease in the tea's temperature ?
A certain substance has a mass per mole of When is added as heat to a sample, the sample's temperature rises from to . What are the
(a) specific heat and
(b) molar specific heat of this substance ?
(c) How many moles are in the sample ?
A common window is to be replaced with a better insulated one. The initial window has glass with thickness . The new window has two such glass layers, separated by , with the intermediate space containing air. For
(a) the common window and
(b) the replacement.
Find the energy loss in watts per square meter when the outside temperature is and the inside temperature is . (Given for glass thermal conductivity )
One way to keep the contents of the garage from becoming too cold at night when there is a severe subfreezing temperature in the forecast is to put a tube of water inside the garage. If the mass of the water is and its initial temperature is ,
(a) How much energy must the water transfer to its surrounding in order to freeze completely? and
(b) What is the lowest possible temperature of the water and its surrounding until that happens?
Non-metric version:
(a) How long does a water heater take to raise the temperature of gal of water from to ?
Metric version:
(b) How long does a water heater take to raise the temperature of of water from to ? [Take specific heat of water , for water at , ]
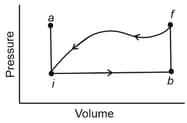
A lab sample of gas is taken through cycle shown in the diagram, net work done is . Along path , the change in the internal energy is and the magnitude of the work done is . Along path the energy transferred to the gas as heat is . How much energy is transferred as heat along
(a) path and
(b) path ?
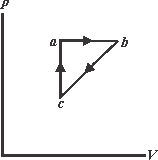
When a system is taken from state to state along path . In the figure and . Along the path .
(a) What is along the path ?
(b) If for the return path , what is the for this path?
(c) If . What is ?
If , what is for,
(d) path and
(e) path ?
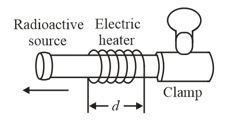
In a certain experiment, a small radioactive source must move at selected and extremely slow speed. This motion is accomplished by fastening the source to one end of an aluminum rod and heating the central section of the rod in a controlled way. If the effective heated section of the rod in given figure has length , then at what constant rate must the temperature of the rod be changed, when the source is to be moved at a constant speed ?