S K Gupta and Anubhuti Gangal Solutions for Chapter: Area of a Trapezium, a Polygon and Semicircle, Exercise 2: Exercise 21(A)
S K Gupta Mathematics Solutions for Exercise - S K Gupta and Anubhuti Gangal Solutions for Chapter: Area of a Trapezium, a Polygon and Semicircle, Exercise 2: Exercise 21(A)
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 21: Area of a Trapezium, a Polygon and Semicircle, Exercise 2: Exercise 21(A) with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. ICSE NUMBERS WIZ solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from S K Gupta and Anubhuti Gangal Solutions for Chapter: Area of a Trapezium, a Polygon and Semicircle, Exercise 2: Exercise 21(A) with Hints & Solutions
The area of a trapezium is . The perpendicular distance between the two parallel sides is . If the difference of the parallel sides is , find the length of the parallel sides.
The lengths of the parallel sides of a trapezium are in the ratio and the distance between them is . If the area of trapezium is , find the lengths of its parallel sides.
Two parallel sides of an isosceles trapezium are and respectively. If the length of each non-parallel side is , find the area of the trapezium.
is a trapezium of area . is parallel to and is longer than by . If the distance between and is , find and .
Find the cost of watering a trapezoidal field whose parallel sides are and respectively, the perpendicular distance between them is and the rate of watering is .
The parallel sides of a trapezium are and , its non-parallel sides are equal, each being. Find the area of the trapezium.
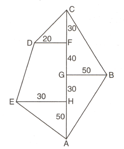
In the figure, and are parallel sides of a trapezium and . Given, and diagonal , calculate the area of trapezium
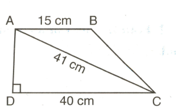
Find the area of the pentagonal field shown alongside.
All dimensions are in metres.