Refraction of Light
Important Questions on Refraction of Light
The image below shows the refraction of light in three transparent rectangular blocks, X, Y and Z, made of different materials when they are placed in air. The angle of incidence is different in each case but the angle of refraction is the same in all three blocks.
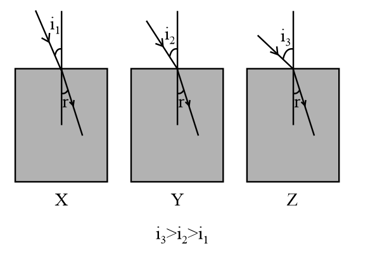
Compare the speed of light in the three blocks. Justify your answer.
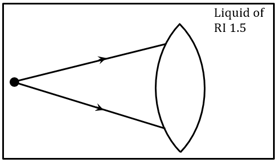
A lens made of material with a refractive index is immersed in a liquid with a refractive index . The diagram below shows two rays incident on the lens when it is immersed in the liquid.
Copy the diagram and draw the light rays after they pass through the lens. Justify your diagram.
The images formed by an ordinary convex lens suffer from a defect, called chromatic defect, which leads to false coloured edges in the images. This happens because light rays of different colours bend differently as they enter and leave the lens.
If a parallel white light beam passes through a convex lens, the light of which colour (among violet to red in the spectrum) will converge at a point closest to the lens? Justify your answer.
When a lens in placed at Q, a sharp image is formed on the screen. The image formed is real, inverted and diminished. When the lens is moved to P, another sharp image is formed on the screen.
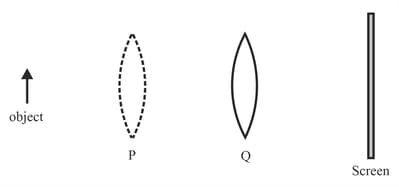
What is the nature of the image formed when the lens is at P?
When an incident ray of light enters a medium from the air, it bends towards the normal. Which of the following is TRUE about the refractive index of the medium () as compared to the refractive index of air ()?
Two convex lenses P and Q have focal length and respectively. Which of the following is TRUE about the combined power of the two lenses?
The eyeball of a person has become slightly larger. Which kind of lens should the person wear to correct the defect in the vision caused by this change in size of the eyeball?
A spherical lens forms three times magnified real image of an object placed in front of the lens. If the object is moved towards the lens through , five times magnified virtual image is obtained. Then
You are in a dark room. You have a box containing some lenses. Only one of them is a converging lens. Describe how, by just feeling the lenses, you can pick out the converging lens.
A lens may have two spherical surfaces, bulging outwards. Such a lens is called a convex lens. It is thicker at the middle as compared to the edges. A concave lens is bounded by two spherical surfaces, curved inwards. It is thicker at the edges than at the middle. Answer the following question.
The nature of images formed by two lenses are given.
(i) An erect and magnified virtual image
(ii) An erect and diminished virtual image
What type of lens is used in the first case?
The ratio between the speed of light in medium to speed in vacuum is the refractive index. When light travels in a medium other than the vacuum, the atoms of that medium continually absorb and re-emit the particles of light, slowing down the speed of light.
The refractive index of glass is . The critical angle of the glass is,
A small object is placed in front of convex lens of focal length , such that a virtual image is formed at a distance of . The magnification produced is
(Choose From: )
Light travels from air to glass slab having refractive index of . What will be the speed of light in glass in the order of in ? Speed of light in vacuum is .
A student obtained a sharp image of the grill of a window on a screen using a convex lens. For better results, the teacher suggested focussing of a distant tree instead of the grill. In what direction should the lens be moved for this purpose?
Find the power (in ) of a concave lens of focal length .
is the speed of light in a transparent medium which has a refractive index of . Find the value of . (The speed of light in vacuum is ).
An object is placed at a distance of from a convex lens of focal length . Find the position and nature of the image formed.
The degree of convergence or divergence of light rays achieved by a lens is expressed in terms of its power. The power, of a lens is given by the relation,
where, is the focal length of the lens in metres.
Many optical instruments use a number of lenses. These lenses are combined to increase the magnification and sharpness of the images produced. The resultant or net power of the combination of lenses placed in contact with each other is given by the algebraic sum of the individual powers of each of the lenses. If the individual powers of two lenses are and , the resultant power, is given by
The focal length, of the combination of two lenses of focal lengths and is given by
Suppose you are given three lenses and with focal lengths and . and are convex lenses whereas is a concave lens. The three lenses are kept in contact with each other.
On the basis of the above information and what you have studied in the course, answer the following questions:
The combination behaves as a
The degree of convergence or divergence of light rays achieved by a lens is expressed in terms of its power. The power, of a lens is given by the relation,
where, is the focal length of the lens in metres.
Many optical instruments use a number of lenses. These lenses are combined to increase the magnification and sharpness of the images produced. The resultant or net power of the combination of lenses placed in contact with each other is given by the algebraic sum of the individual powers of each of the lenses. If the individual powers of two lenses are and , the resultant power, is given by
The focal length, of the combination of two lenses of focal lengths and is given by
Suppose you are given three lenses and with focal lengths and . and are convex lenses whereas is a concave lens. The three lenses are kept in contact with each other.
On the basis of the above information and what you have studied in the course, answer the following question:
The power of the combination of lenses is
Mala can see the objects lying between and from her eye. Her vision can be corrected by using the lens of power . Is the statement true or false?