Excretion in Animals
Important Questions on Excretion in Animals
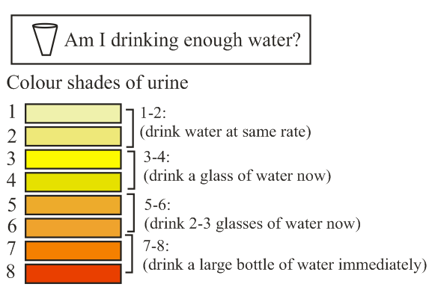
Under normal conditions, human urine contains 95% water and 5% waste products. What would be the percentage of waste products in a darker shade of urine?
The picture shows different colour shades of urine.
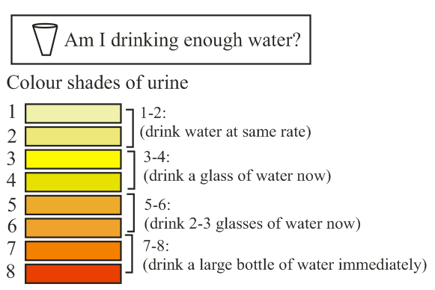
Which colour shade indicates that the body is well hydrated?
Does the body produce more urine on a cold day rather than a hot day if the same amount of water is consumed?
Draw a labelled diagram of human excretory system.
Our body produces more urine during winters but less urine in summers, although we drink more water in summers as compared to winters. Why?
The afferent arteriole is the arteriole that brings blood to the glomerulus. The efferent arteriole is the arteriole that carries blood away from the glomerulus. The diameter of the efferent arteriole is less than that of the afferent arteriole. What will be the consequences if the opposite structural quality will be performed by them?
Name the excretory organs in the following organisms. Select your answers from the words given below.
(Flame cells, Contractile vacuoles, Kidneys, Malpighian tubules, Nephridia)
- Amoeba, Paramecium
- Human and other vertebrates
- Tapeworm, liver fluke.
- Earthworm, leech
- Spiders, cockroach
Solve the crossword puzzle with the help of the clues given below:

Across
4. Food conducting tissue in plants. (6)
8. The rhythmic contraction and expansion of the heart. (9)
9. The technique used for removing toxic materials from the blood, when the kidneys are not functioning. (8)
10. The pigment in red blood cells. (11)
11. Muscular organ present in the chest cavity taking part in the transport of blood. (5)
14. Loss of water in vapour form of the leaves. (13)
15. The upper chambers of the heart. (8)
16. Water conducting tissue in plants. (5)
17. Removal of waste materials from the body. (9)
18. Bean-shaped structure taking part in excretion. (6)
19. Blood vessels which carry CO2 rich blood from different parts of the body. (5)
Down:
1. The term for the lower chambers of the heart. (10)
2. The throbbing of the arteries. (5)
3. The fluid flowing in blood vessels. (5)
5. Blood vessels which carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart. (8)
6. The fluid part of the blood. (6)
7. The tissue in plants which transports water, nutrients and food. (8, 6)
12. The channels in which blood flows. (5, 7)
13. Fine blood vessels which form a connection between arteries and veins. (11)
Arjun was involved in an accident and his Kidneys got damaged. How will this affect him?
A researcher in Chennai wants to study how much carbohydrate is burnt up in the body in a long-distance race. She measured the body weights of athletes before and after a 2 km race. She found to her surprise that each athlete lost 1 kg or more. The athletes could not have burnt 1 kg carbohydrates in their bodies in a 2 km race, she thought.
Do you think she had designed the experiment properly?
What processes take place during the period when the blood enters the kidneys till the urine leaves the body?
You have studied in the chapter that due to certain abnormal conditions, the kidneys can fail. Is it possible for a person to survive with one kidney? How can such people be cured?
There is a pair of bean-shaped organs P in the human body towards the back, just above the waist. A waste product Q formed by the decomposition of unused proteins in the body is brought into organs P through the blood. The numerous tiny filters R present inside the organs P clean the dirty blood by removing the waste product Q. If due to some reason, the organs P of a person stop functioning completely, the person's blood can be cleaned periodically by a process S to save his life. What are P, Q, R, and S?
What is the difference between ureotelic and uricotelic?
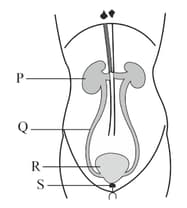
In the given diagram, which part of the excretory system consists of nephrons?
We perspire more in summer days. Why is it so? Name the body organ, which helps in perspiration.
Science Quiz/Puzzle:
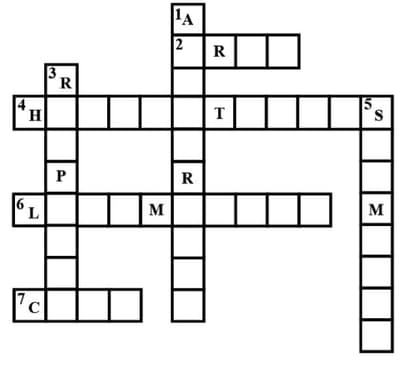
Across
2. Waste expelled by kidneys as urine.
4. Organisms that feed on plants or other organisms.
6. Movement from one place to another shown by animals.
7. The basic unit of structure and function of organisms.
Down
1. They make their own food.
3. Reaction of organisms to some external change.
5. A change that evokes a response in organisms.

