Subject Experts Solutions for Chapter: Sound, Exercise 2: PRACTICE QUESTIONS (COMPETITION WING)
Subject Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Subject Experts Solutions for Chapter: Sound, Exercise 2: PRACTICE QUESTIONS (COMPETITION WING)
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 5: Sound, Exercise 2: PRACTICE QUESTIONS (COMPETITION WING) with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Pearson IIT Foundation Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Subject Experts Solutions for Chapter: Sound, Exercise 2: PRACTICE QUESTIONS (COMPETITION WING) with Hints & Solutions
Three persons , , and are at different points A, B, and C, respectively, as shown in the figure. Two persons and clap at the same time. Which among the following can be the minimum distance between and to hear the clap sound distinctly? (Take the velocity of sound in air as )

The audible range of frequency is to . Determine the corresponding range of time periods of vibrations.
A bat entering into a well finds it difficult to come out of it. Explain the reason.
Ramu and Numu are celebrating Diwali with crackers when Ramu fired a cracker after looking at the lighting Numu started counting seconds hand movement in his watch at and he stopped counting when he heard the cracker sound at . Find the distance between Ramu and Numu if the speed of the sound is .
A student breaks a fused bulb, and then hears a sound of explosion. What could be the reason for this? Explain.
How are dogs made alert by the crime department? Explain.
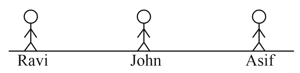
Three boys Ravi, John, and Asif stand in a straight line as shown in the figure. Ravi and Asif fire crackers at the same instant of time. John hears the first sound after and the second sound after . Determine the distance between Ravi and Asif. The velocity of sound in air is
A child pushed his cradle for play and started learning numbers by counting the oscillations of his cradle. He counted one number per one oscillation starting from , then find the number of numbers the child learned and cradle frequency of oscillations for the total time of second, if the time period of the cradle is .
