Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Elasticity, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking
Umakant Kondapure Physics Solutions for Exercise - Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Elasticity, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 13: Elasticity, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. MHT-CET TRIUMPH Physics Multiple Choice Questions Part - 1 Based on Std. XI & XII Syllabus of MHT-CET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Elasticity, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking with Hints & Solutions
The modulus of elasticity is dimensionally equivalent to
One end of a horizontal thick copper wire of length and radius is welded to an end of another horizontal thin copper wire of length and radius . When the arrangement is stretched by applying forces at two ends, the ratio of the elongation in the thin wire to that in the thick wire is
A thick rope of density and length is hung from a rigid support. The increase in length of the rope due to its own weight is is Young's modulus)
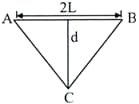
A wire of length and radius is stretched between A and B without the application of any tension. If is Young's modulus of the wire and it is stretched like ACB, then the tension in the wire will be
(Consider )
A wire elongates by when a load is hanged from it. If the wire goes over a pulley and two weights , each hung at the two ends, the elongation of the wire will be (in )
A pendulum made of a uniform wire of cross-sectional area has time period . When an additional mass is added to its bob, the time period changes to . If the Young's modulus of the material of the wire is then is equal to gravitational acceleration)
Two rods of different materials having coefficients of linear expansion and Young's modulii and respectively are fixed between two rigid massive walls. The rods are heated such that they undergo the same increase in temperature. There is no bending of rods. If the thermal stress developed in the two rods are equally provided. is equal to
The stress along the length of a rod (with rectangular cross-section) is 1% of the Young's modulus of its material. What is the approximate percentage of change of its volume? (Poisson's ratio of the material of the rod is 0.3)
