Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Surface Tension, Exercise 4: Evaluation Test
Umakant Kondapure Physics Solutions for Exercise - Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Surface Tension, Exercise 4: Evaluation Test
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 14: Surface Tension, Exercise 4: Evaluation Test with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. MHT-CET TRIUMPH Physics Multiple Choice Questions Part - 1 Based on Std. XI & XII Syllabus of MHT-CET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Surface Tension, Exercise 4: Evaluation Test with Hints & Solutions
Suppose $64$ raindrops combine to form a single drop. Calculate the ratio of the total surface energy of the $64$ drops to that of a single drop.
Two separate air bubbles (radii and formed of same liquid (Surface tension ) come together to form a double bubble. Find the radius of curvature in of the internal film surface common to both the bubbles.
Two soap bubbles and are kept in a closed chamber where the air is maintained at pressure The radii of bubbles and are and respectively. Surface tension of the soap water used to make bubbles is Find the ratio where and are the no. of moles of air in bubbles A and B, respectively [Neglect effect of gravity]
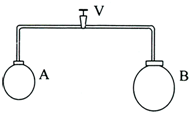
The valve in the bent tube is initially kept closed. Two soap bubbles A(smaller) and B(larger) are formed at 2 open ends of the tube. is now opened, and air can flow freely between the bubbles.
Two parallel glass plates are held vertically at a small separation d and dipped in a liquid of surface tension the angle of contact and density . The height of water that climbs up in the gap between glass plates is given by
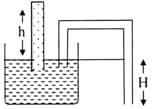
Two capillary tubes of same radius are lowered into a vessel with water as shown. The water in the straight tube rises to a height 'h'. The lower end of bent tube is at a depth 'H' below the level of the water in the vessel. What will the level of water be in bent tube and what form will the meniscus take? The incorrect option for the given situation is
When a loop of wire is dipped in a wetting liquid and is taken out. A liquid film is formed and a loop of light inextensible thread is gently put on the liquid film. A hole is pricked inside the loop of thread. Due to property of surface tension, free surface of the liquid tries to minimize its surface area and hence area of the hole will be maximized. In the above description, loop wire is square of side units. If length of thread is units, what is the final surface area for soap film on one side of wire frame? (Neglect the friction everywhere)
When a loop of wire is dipped in a wetting liquid and is taken out. A liquid film is formed and a loop of light inextensible thread is gently put on the liquid film. A hole is pricked inside the loop of thread. Due to property of surface tension, free surface of the liquid tries to minimize its surface area and hence area of the hole will be maximized. In the above description, loop wire is square of side 4 units, liquid is soap and length of loop of thread is 15 units. If the surface tension of soap is 'S', what is the tension in the thread?
