Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking
Umakant Kondapure Physics Solutions for Exercise - Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 8: Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. MHT-CET TRIUMPH Physics Multiple Choice Questions Part - 2 Based on Std. XI & XII Syllabus of MHT-CET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking with Hints & Solutions
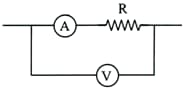
In the circuit shown below, the ammeter and the voltmeter readings are and respectively. Then the value of the resistance is
The deflection in galvanometer falls to $\left(\frac{1}{4}\right)^{\operatorname{th}}$ when it is shunted by . If additional shunt of is connected to earlier shunt, the deflection in galvanometer falls to
A voltmeter of range having a resistance of is converted into an ammeter of range. The value of necessary shunt is (nearly)
A cyclotron is used to accelerate protons, deuterons, $\alpha$ -particles, etc. If the energy attained, after acceleration, by the protons is the energy attained by $\alpha$ -particles shall be
An alternating electric field of frequency '' is applied across the dees (radius ) of a cyclotron to accelerate protons (mass ). The operating magnetic field used and of the proton beam produced by it are respectively ( charge on proton)
A proton, an alpha particle both enter a region of uniform magnetic field , moving at right angles to the field . If the radius of circular orbits for both the particles is equal and the kinetic energy acquired by proton is , the energy acquired by alpha particle will be:
An electron revolves along a circular path of radius with constant angular velocity about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the circle. If the external magnetic field is absent, then the potential difference between the centre of the circle and a point on the circumference of the circle is (mass of the electron ),
A light charged particle is revolving in a circle of radius '' in electrostatic attraction of a static heavy particle with opposite charge. How does the magnetic field '' at the centre of the circle due to the moving charge depend on '' ?
