Normal Modes of a String
Important Questions on Normal Modes of a String
Two pulses of identical shape overlap such that the displacement of the rope is momentarily zero at all points. What happens to the energy at this time?
A string fastened at both ends has successive resonances with wavelengths of for the harmonic and for the harmonic.
(a) Which harmonics are these?
(b) What is the length of the string?
(c) What is the wavelength of the fundamental frequency?
A rope long is fixed at one end and tied to a light string of the same length at the other end. Its tension is .
(a) What are the wavelengths of the fundamental and the first two overtones?
(b) What are the frequencies of these standing waves?
[Note: In this case, fixed end is a node and the end tied with the light string is antinode.]
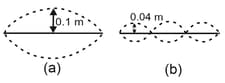
Figure shows different standing wave patterns on a string of linear mass density under a tension of . The amplitude of antinodes is indicated in each figure. The length of the string is .
(i) Obtain the frequencies of the modes shown in figures and .
(ii) Write down the transverse displacement as a function of and for each mode. (Take the initial configuration of the wire in each mode to be as shown by the dark lines in the figure).
A wire with mass is stretched so that its ends are tied down at points apart. The wire vibrates in its fundamental mode with frequency and with an amplitude at the antinodes of .
(a) What is the speed of propagation of transverse wave in the wire?
(b) Compute the tension in the wire.
(c) Find the maximum transverse velocity and acceleration of particles in the wire.
A long rope is stretched between two supports with a tension that makes the speed of transverse waves . What are the wavelength and frequency of
(a) the fundamental?
(b) the second overtone?
(c) the fourth harmonic?
A guitar string is long and has a fundamental frequency of . Where should it be pressed to produce a fundamental frequency of ?
A sonometer wire has a total length of between the fixed ends. Where should the two bridges be placed below the wire so that the three segments of the wire have their fundamental frequencies in the ratio ?
A string vibrates in segments to a frequency of .
(a) What is its fundamental frequency?
(b) What frequency will cause it to vibrate into segments?
The vibrations from an tuning fork set up standing waves in a string clamped at both ends. The wave speed in the string is known to be for the tension used. The standing wave is observed to have four antinodes. How long is the string?
A wire having a linear density of is stretched between two rigid supports with a tension of . It is observed that the wire resonates at a frequency of . The next higher frequency at which the same wire resonates is . Find the length of the wire.
A guitar string under a tension of has a mass per unit length of What is the highest resonance frequency of the string that can be heard by a person able to hear frequencies upto ?
A string vibrates in its first normal mode with a frequency of . The vibrating segment is long and has a mass of .
(a) Find the tension in the string.
(b) Determine the frequency of vibration, when the string vibrates in three segments.
Find the fundamental frequency and the next three frequencies that could cause a standing wave pattern on a string that is long has a mass per unit length of and is stretched to a tension of .
The period of oscillations of a point is and the velocity of propagation of oscillation is . The difference of phases between the oscillations of two points at distance and , respectively, from the source of oscillations is
Three resonant frequencies of string with both rigid ends are and . If the length of the string is , what is the speed of the transverse wave in the string?
For a certain stretched string, three consecutive resonance frequencies are observed as and , respectively. Then, the fundamental frequency is
If and are the wavelength of the waves giving resonance to the fundamental, first and second overtone modes, respectively, in a string fixed at both ends. The ratio of the wavelengths is
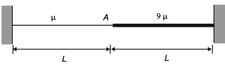
A light string is tied at one end to fixed support and to a heavy string of equal length at the other end as shown in figure. Mass per unit length of the strings are and and the tension is Find the possible values of frequencies such that point is a node/antinode.
Three pieces of string, each of length , are joined together end-to-end, to make a combined string of length . The first piece of string has a mass per unit length the second piece has a mass per unit length and the third piece has a mass per unit length
If the combined string is under tension , how much time does it take a transverse wave to travel the entire length Give your answer in terms of and .
Does your answer to part (a) depend on the order in which the three pieces are ioined together? Explain.