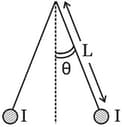
Two long currents carrying thin wires, both with current , are held by insulating threads of length L and are in equilibrium as shown in the figure, with threads making an angle ' ' with the vertical. If wires have a mass per unit length then the value of is:
( gravitational acceleration)

Important Questions on Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
A rectangular loop of sides and , carrying a current of , is placed in different orientations as shown in the figure below.
(a) 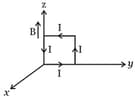 (b)
(b) 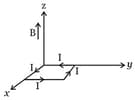
(c) 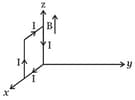 (d)
(d) 
If there is a uniform magnetic field of in the positive direction, in which orientations the loop would be in stable equilibrium and unstable equilibrium?
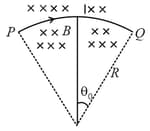
A wire carrying current is tied between points and and is in the shape of a circular arc of radius due to a uniform magnetic field (perpendicular to the plane of the paper, as shown in the figure) in the vicinity of the wire. If the wire subtends an angle at the center of the circle (of which it forms an arch) then the tension in the wire is:
A short bar magnet is placed in the magnetic meridian of the earth with North Pole pointing north. Neutral points are found at a distance of from the magnet on the East-West line, drawn through the middle point of the magnet. The magnetic moment of the magnet in is close to:
(Given in SI units and Horizontal component of earth's magnetic field Tesla.)
Two long straight parallel wires, carrying (adjustable) currents and , are kept at a distance apart. If the force between the two wires is taken as 'positive' when the wires repel each other and 'negative' when the wires attract each other, the graph showing the dependence of , on the product , would be:

