HARD
Earn 100
A container is filled with moles of an ideal diatomic gas at absolute temperature When heat is supplied to gas temperature remains constant but moles dissociates into atoms. Heat energy supplied to gas is?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Thermodynamics
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
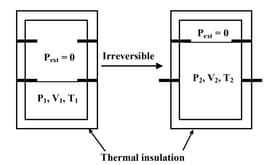
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
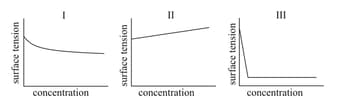
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
The quantity of heat (in ) required to raise the temperature of of ethanol from to the boiling point and then change the liquid to vapor at that temperature is closest to [Given, boiling point of ethanol . Specific heat capacity of liquid ethanol . Latent heat of vaporisation of ethanol ]
EASY
(Latent heat of ice is and )
MEDIUM
The combination of plots which does not represent isothermal expansion of an ideal gas is
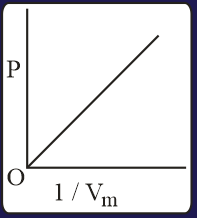
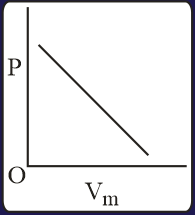
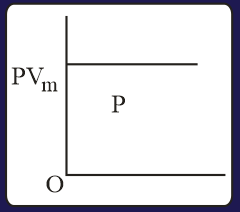
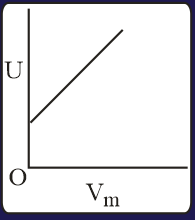
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
(a) Internal energy and enthalpy each depends on temperature.
(b) Compressibility factor is not equal to 1
(c)
(d) for any process
MEDIUM

