A gas is said to behave like an ideal gas when relation constant. When do you expect real gas to behave like an ideal gas?
A gas is said to behave like an ideal gas when relation constant. When do you expect real gas to behave like an ideal gas?
When both the temperature and pressure are low.
When the temperature is high and pressure is low.
When both the temperature and pressure are high.
When the temperature is low.
Important Questions on States of Matter
( is universal gas constant and is the acceleration due to gravity)
The volume of gas is twice than that of gas . The compressibility factor of gas is thrice than that of gas at same temperature. What are the pressures of the gases for equal number of moles?
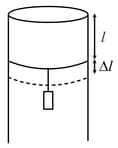
A long cylindrical pipe of radius is closed at its upper end and has an airtight piston of negligible mass as shown. When mass is attached to the other end of piston, it moves down by a distance, before coming to equilibrium. Assuming air to be an ideal gas, (see figure) is close to , one atmospheric pressure is ),
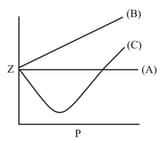
The variation of the compressibility factorwith pressure for some gases, are shown in the figure below. Identify the gases and .