MEDIUM
Earn 100
Explain London dispersion forces.
Important Questions on States of Matter: Gaseous and Liquid States
EASY
(Latent heat of ice is and )
EASY
EASY
Increasing order of boiling points in the following compounds is:
MEDIUM
The combination of plots which does not represent isothermal expansion of an ideal gas is
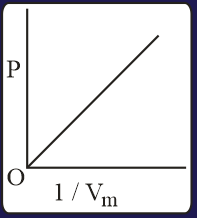
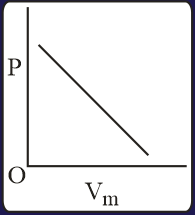
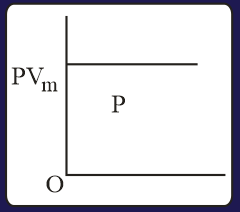
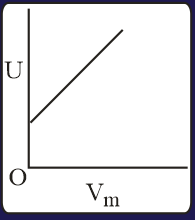
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM
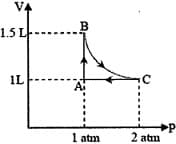
MEDIUM
In which of the following solid substance dispersion forces exist?
HARD
HARD
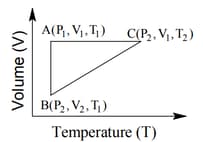
The correct option(s) is (are)
MEDIUM
Match the type of interaction in column with the distance dependence of their interaction energy in column
| A | B |
| (i) ion - ion | (a) |
| (ii) Dipole - dipole | (b) |
| (iii) London dispersion | (c) |
| (d) |
HARD
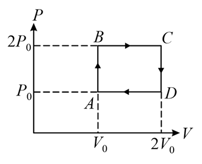
The above diagram represents the thermodynamic cycle of an engine, operating with an ideal mono-atomic gas. The amount of heat, extracted from the source in a single cycle, is:
MEDIUM
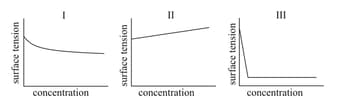
MEDIUM
(R = 8.314 J/mol K) (ln7.5 = 2.01)
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
Given:
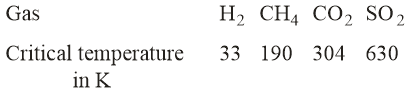
On the basis of data given above, predict which of the following gases shows the least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal?

