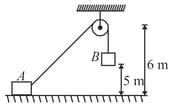
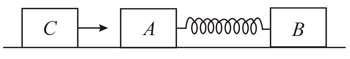'' block of mass is held at rest on a smooth horizontal floor. A light frictionless, small pulley is fixed at a height of from the floor. A light inextensible string of length , connected with passes over the pulley and another identical block is hung from the string. Initial height of is from the floor as shown in figure. When the system is released from rest, starts to move vertically downwards and slides on the floor towards right. (i) If at an instant string makes an angle with horizontal, calculate relation between velocity of and of B (ii) Calculate when strikes the floor.


Important Questions on Work, Energy and Power
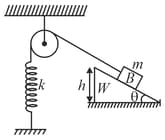
In the figure shown the pulley is smooth. The spring and the string are light. The block '' slides down from the along the fixed rough wedge of inclination . Assuming that the block reaches the end of the wedge. Find the speed of the block at the end. Take the coefficient of friction between the block and the wedge to be and the spring was relaxed when the block was released from the top of the wedge.
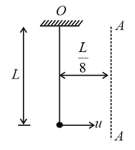
As shown in the figure a person is pulling a mass '' from ground on a fixed rough hemispherical surface upto the top of the hemisphere with the help of a light inextensible string. Find the work done by tension in the string if radius of hemisphere is and friction co-efficient is . Assume that the block is pulled with negligible velocity.
The sphere from rest when strikes a block mass of placed on a rough horizontal plane and comes to rest after collision. The block comes to rest after moving a distance of . Find of ground & block & coefficient of restitution .
A man whose mass is jumps vertically into air from a sitting position in which his centre of mass is at a height from the ground. When his feet are just about to leave the ground his centre of mass is from the ground and finally rises to when he is at the top of the jump. What is the average upward force exerted by the ground on him?
Two bodies and of masses and respectively are placed on a smooth floor. They are connected by a spring. A third body of mass moves with velocity along the line joining and and collides elastically with as shown in figure. At a certain instant of time after collision, it is found that the instantaneous velocities of and are the same. Further at this instant the compression of the spring is found to be . Determine -
(ii) the spring constant,