(6) (b) This is a graph of magnetic flux density through a turn coil with a cross-sectional area against time.
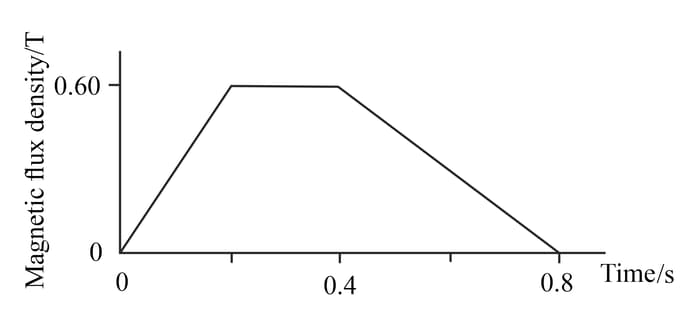
(ii) Determine the maximum magnitude of the induced e.m.f. in the coil.


Important Questions on Electromagnetic Induction
(6) (b) This is a graph of magnetic flux density through a turn coil with a cross-sectional area against time.
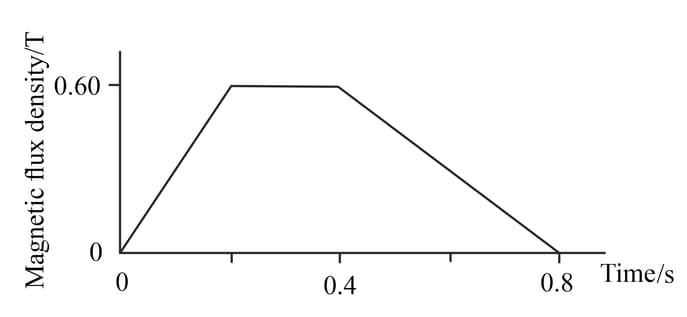
(iii) Sketch a diagram to show the induced e.m.f. varies with time. Mark values on both the and time axes.
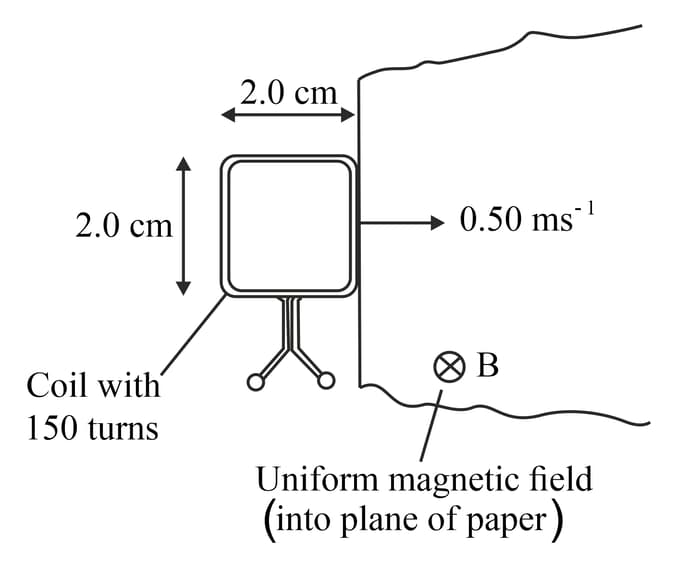
This diagram shows a square coil about to enter a region of uniform magnetic field of magnetic flux density The magnetic field is at right angles to the plane of the coil. The coil has turns and each side is in length. The coil moves at a constant speed of
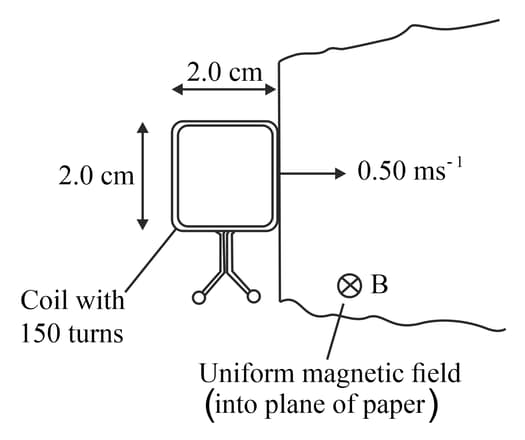
(a) (i) Calculate the time taken for the coil to completely enter the region of magnetic field.
This diagram shows a square coil about to enter a region of uniform magnetic field of magnetic flux density The magnetic field is at right angles to the plane of the coil. The coil has turns and each side is in length. The coil moves at a constant speed of
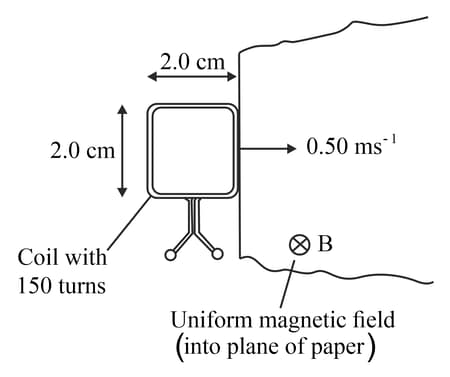
(a) (ii) Determine the magnetic flux linkage through the coil when it is all within the region of magnetic field
This diagram shows a square coil about to enter a region of uniform magnetic field of magnetic flux density The magnetic field is at right angles to the plane of the coil. The coil has turns and each side is in length. The coil moves at a constant speed of
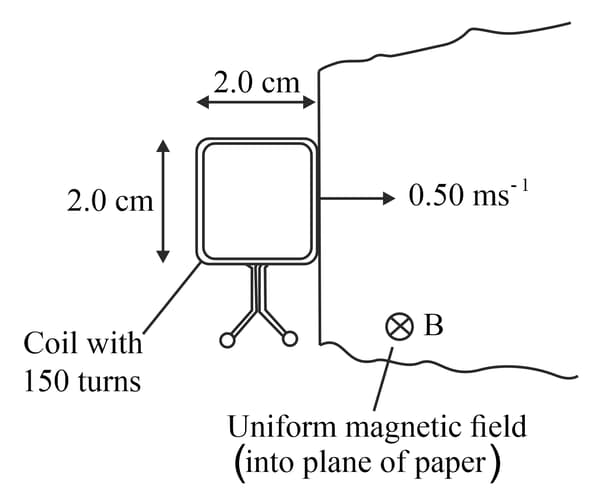
(b) Explain why the magnitude of the induced e.m.f. is constant while the coil is entering the magnetic field.
This diagram shows a square coil about to enter a region of uniform magnetic field of magnetic flux density The magnetic field is at right angles to the plane of the coil. The coil has turns and each side is in length. The coil moves at a constant speed of
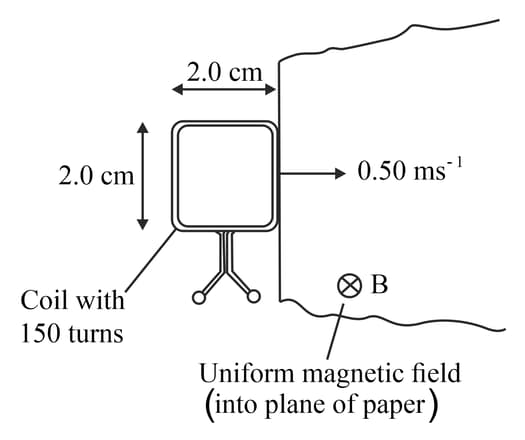
(c) Determine the induced e.m.f. across the ends of the coil.
This diagram shows a square coil about to enter a region of uniform magnetic field of magnetic flux density The magnetic field is at right angles to the plane of the coil. The coil has turns and each side is in length. The coil moves at a constant speed of
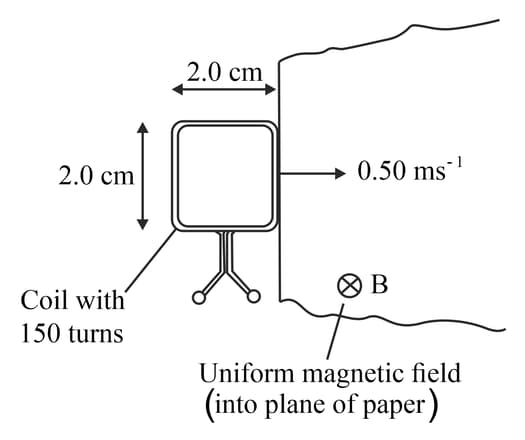
(d) Explain the induced e.m.f. across the ends of the coil when it is completely within the magnetic field
This diagram shows a square coil about to enter a region of uniform magnetic field of magnetic flux density The magnetic field is at right angles to the plane of the coil. The coil has turns and each side is in length. The coil moves at a constant speed of
(e) from the instant that the coil enters the magnetic field. Your time axis should go from
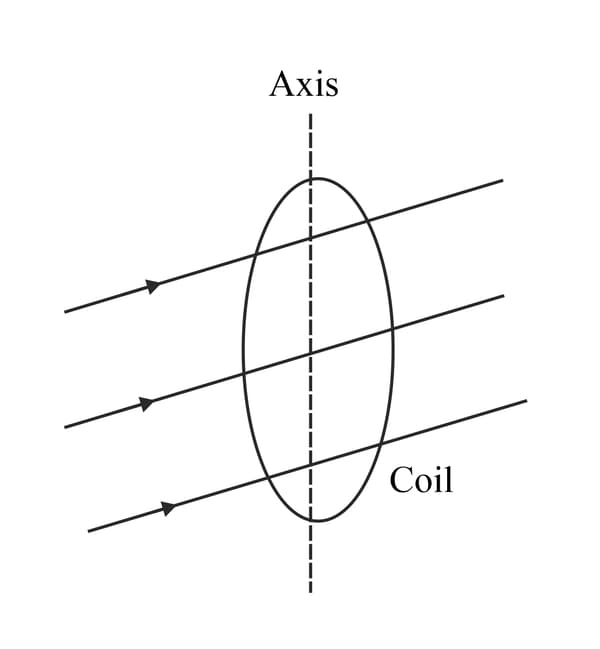
(a) State Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.