(a) A point charge is located at distance from an infinite plane. Determine the electric flux through the plane due to the point charge.
(b) A point charge is located at a very small distance from the center of a very large square on the line perpendicular to the square passing through its center. Determine the approximate electric flux through the square due to the point charge.

Important Questions on Electric Flux and Gauss's Law
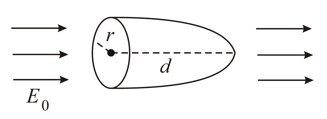
Calculate the total electric flux through the paraboloidal surface due to a uniform electric field of magnitude in the direction shown in figure.
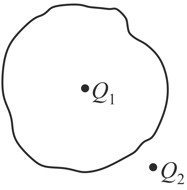
Consider a closed surface of arbitrary shape as shown in figure. Suppose a single charge , is located at some point, within the surface and the second charge is located outside the surface.
(a) What is the total flux passing through the surface due to charge ?
(b) What is the total flux passing through the surface due to charge ?
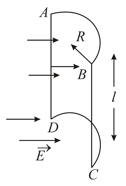
A hollow half-cylinder surface of radius and length is placed in a uniform electric field . Electric field is acting perpendicular on the plane . Find the flux through the curved surface of the hollow cylindrical surface.
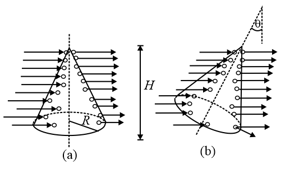
A cone of radius and height is placed in an uniform electric field as shown in the figure (a), if the axis of the cone made inclined with the vertical as shown in the figure (b). Calculate the flux of electric field entering the cone.
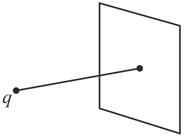
Point charge is placed at a point on the axis of a square non-conducting surface. The axis is perpendicular to the square surface and is passing through its centre. The flux of Electric field through the square caused due to charge is . If the square is given a surface charge of uniform density , find the magnitude of the force on the square surface due to point charge .
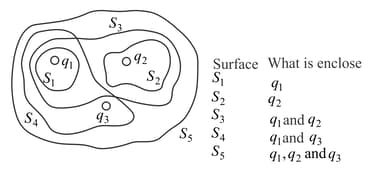
The three small spheres as shown in figure carry charges and . Find the net electric flux through each of the following closed surfaces shown in cross-section in the figure.
(a) , (b) , (c) , (d) , (e)
Do your answers to parts from (a) to (e) depend on how the charge is distributed over each small sphere? Why or why not?
A conducting sphere carrying charge is surrounded by a spherical conducting shell.
(a) What is the net charge on the inner surface of the shell?
(b) Another charge is placed outside the shell. Now, what is the net charge on the inner surface of the shell?
(c) If is moved to a position between the shell and the sphere, what is the net charge on the inner surface of the shell?
(d) Are your answers valid if the sphere and shell are not concentric?
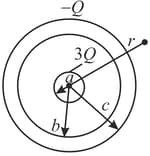
A solid insulating sphere of radius carries a net positive charge , uniformly distributed throughout its volume. Concentric with this sphere is a conducting spherical shell with an inner radius and outer radius and having a net charge , as shown in the figure.
(a) Consider a spherical Gaussian surface of radius , the net charge enclosed by this surface is _____.
(b) The direction of the electric field is ___ .
(c) The electric field at is _____.
(d) The electric field in the region with radius , where , is _____.
(e) Consider a spherical Gaussian surface of radius , where , the net charge enclosed by this surface is _____.
(f) Consider a spherical Gaussian surface of radius , where , the net charge enclosed by this surface is _____.
(g) The electric field in the region is _____.
(h) Consider a spherical Gaussian surface of radius . Find an expression for the net charge enclosed by this surface as a function of . Note that the charge inside this surface is less than .
(i) The electric field in the region is _____.
(j) The charge on the inner surface of the conducting shell is _____.
(k) The charge on the outer surface of the conducting shell is _____.
(l) Make a plot of the magnitude of the electric field versus .