(a) An X-ray beam, containing X-rays with a variety of frequencies and that has an intensity of , is incident on an aluminium plate of thickness . The average linear attenuation coefficient is .
(i) Calculate the intensity of the transmitted beam.

Important Questions on Medical Imaging
(a) An X-ray beam, containing X-rays with a variety of frequencies and that has an intensity of , is incident on an aluminium plate of thickness . The average linear attenuation coefficient is .
(ii) Explain the advantages of passing the X-rays through this aluminium plate prior to their being incident on a patient.
(c) This is the trace formed on the screen of an oscilloscope when ultrasound is reflected from the front and rear surfaces of the head of a foetus. The time-base of the oscilloscope is set at .
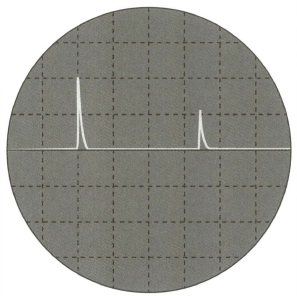
(i) Explain why the second peak is lower than the foetus.
(c) This is the trace formed on the screen of an oscilloscope when ultrasound is reflected from the front and rear surfaces of the head of a foetus. The time-base of the oscilloscope is set at .
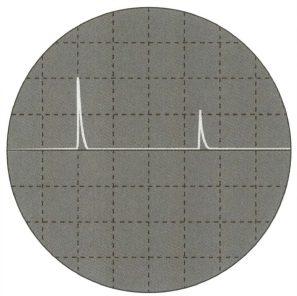
(ii) Calculate the diameter of the head of the foetus.
Outline the theory of the PET scanner.
(b) It is suggested that a scanner could be designed using the annihilation of a proton and an antiproton. Calculate:
(i) the energy released in the proton-antiproton annihilation.
(b) It is suggested that a scanner could be designed using the annihilation of a proton and an antiproton.
(ii) Calculate the wavelength of the -ray photons produced in the annihilation.
