(b) This diagram shows an experiment to measure the speed of a sound in a string. The frequency of the vibrator is adjusted until the stationary wave shown is formed.
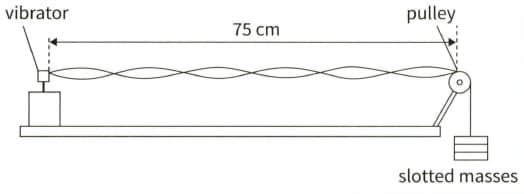
(i) On a copy of the diagram, mark a node (label it N) and an antinode (label it A).


Important Questions on Stationary Waves
(b) This diagram shows an experiment to measure the speed of a sound in a string. The frequency of the vibrator is adjusted until the stationary wave shown is formed.
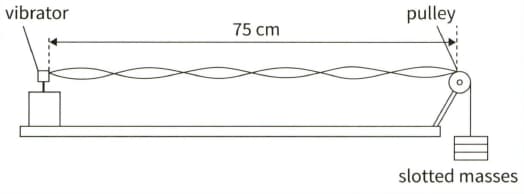
(ii) The frequency of the vibrator is 120Hz. Calculate the speed at which a progressive wave would travel along the string.
This diagram shows a stationary wave, of frequency , produced by a loudspeaker in a closed tube.
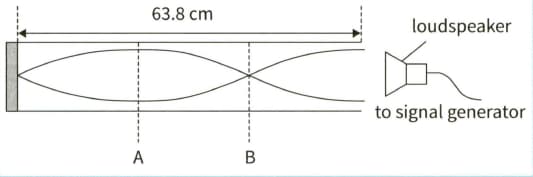
(a) Describe the movement of the air particles at:
(i)
This diagram shows a stationary wave, of frequency , produced by a loudspeaker in a closed tube.
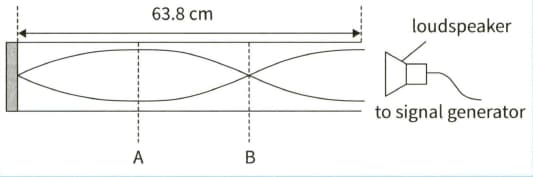
(a) Describe the movement of the air particles at:
(ii)
This diagram shows a stationary wave, of frequency , produced by a loudspeaker in a closed tube.
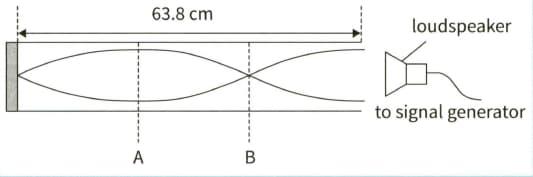
(b) The length the tube is .
Calculate the speed of the sound.
(a) Explain what is meant by:
(i) A coherent source of waves.
(a) Explain what is meant by:
(ii) Phase difference.
(b) A student, experimenting with microwaves, sets up the arrangement shown in this diagram.
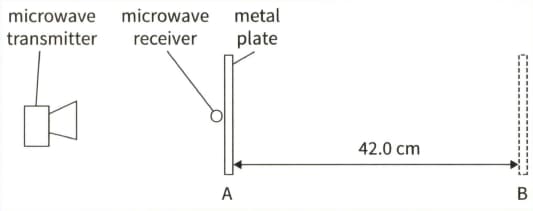
With the metal plate at position there is a very small signal. He slowly moves the plate back, leaving the receiver in the same position. As he does so, he finds that the intensity initially rises until it becomes a maximum, then falls back to a minimum. This cycle repeats a total of five times until the plate reaches position , where once again there is a minimum.
(i) Explain why a series of maxima and minima are heard.
