A Plano-convex lens has a thickness of . When placed on horizontal table, the curved surface in contact with it the apparent depth of the bottom most point of the lens is found to be . If the lens is invested such that the plane face is in contact with the table, the apparent depth of the centre of plane face is found to be . Find the focal length of the lens.

Important Questions on Refraction at Spherical Surfaces and Spherical Lens
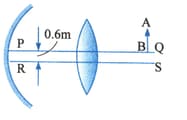
A convex lens of focal length and a concave mirror of focal length are kept with their optic axis and parallel but separated in vertical direction by as shown in Fig. The distance between the lens and mirror is . An upright object of height is placed on the optic axis of the lens at a distance of from the lens. If is the image after refraction from the lens and reflection from the mirror, find the distance from the pole of the mirror and obtain its magnification. Also locate positions of and with respect to optic axis .
A thin biconvex lens of refractive index is placed on a horizontal plane mirror as shown in Fig. The space between the lens and the mirror is then filled with water of refractive index It is found that when a point object is placed above the lens on its principal axis, the object coincides with its own image. On repeating with another liquid, the object and the image again coincide at distance from the lens. Calculate the refractive index of the liquid.
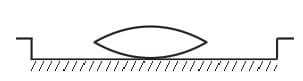
Find the focal length of the lens shown in the figure, Fig. The radii of curvature of both the surfaces are equal to
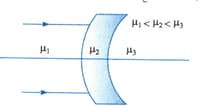
A lens of power is placed in contact with a lens of power . The combination will behave as
