A mass of of ice at is taken from a freezer and placed in a beaker containing of water at . Data for ice and water are given in Table
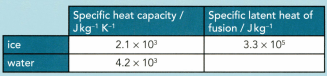
Calculate the amount of thermal energy (heat) needed to convert all the ice at to water at


Important Questions on Thermal Physics
A mass of of ice at is taken from a freezer and placed in a beaker containing 200 g of water at . Data for ice and water are given in Table.
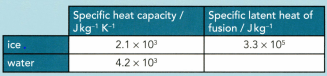
Calculate the final temperature T of the water in the beaker assuming that the beaker has negligible mass.
latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporisation.
An electric heater generating power of is immersed in a beaker of liquid that is placed on a balance. When the liquid begins to boil it is noticed that the mass of the beaker and liquid decreases by every minute.
State how this shows that the liquid is boiling at a steady rate.
An electric heater generating power of is immersed in a beaker of liquid that is placed on a balance. When the liquid begins to boil it is noticed that the mass of the beaker and liquid decreases by every minute.
Calculate a value for the specific latent heat of vaporisation of the liquid.
An electric heater generating power of is immersed in a beaker of liquid that is placed on a balance. When the liquid begins to boil it is noticed that the mass of the beaker and liquid decreases by every minute. State and explain whether the value determined is likely to be larger or smaller than the accepted value.
Explain why energy is needed for boiling even though the temperature of the liquid remains constant.
This diagram shows an apparatus that can be used to measure the specific latent heat of vaporisation of nitrogen.
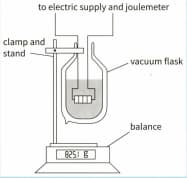
Suggest why the nitrogen is contained in a vacuum flask.
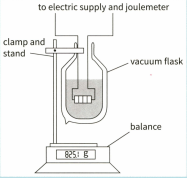
The change in mass of the nitrogen is measured over a specific time interval with the heater switched off. The heater is switched on, transferring energy at , and the change of mass is found once more. The results are shown in the table
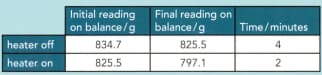
Calculate the specific latent heat of vaporisation of liquid nitrogen.
