EASY
Upper Secondary-IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Explain why we can only calculate a stone's average speed during its fall.

Important Questions on Describing Motion
EASY
Upper Secondary-IGCSE
IMPORTANT
EASY
Upper Secondary-IGCSE
IMPORTANT
EASY
Upper Secondary-IGCSE
IMPORTANT
EASY
Upper Secondary-IGCSE
IMPORTANT
EASY
Upper Secondary-IGCSE
IMPORTANT
EASY
Upper Secondary-IGCSE
IMPORTANT
EASY
Upper Secondary-IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Diagrams in are distance—time graphs for four moving objects. Complete the table by indicating (in the second column) the graph or graphs that represent the motion described in the first column.
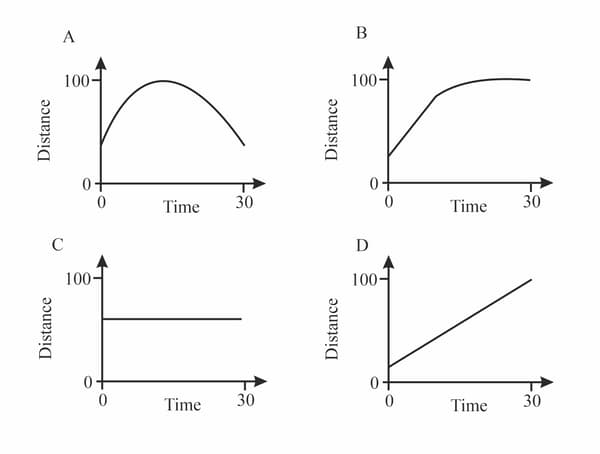
| Description of motion | Graphs |
| Moving at a steady speed | |
| Stationary (not moving) | |
| Slowing down and stopping | |
| Changing speed |
EASY
Upper Secondary-IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Sketch a distance-time graph for the car whose journey is described here.
• The car set off at a slow, steady speed for .
• Then it moved for at a faster speed.
• Then it stopped at traffic lights for before setting off again at a slow, steady speed.
