A mass moving at collides with a mass moving at in the opposite direction. The collision is elastic and head-on. Find the velocity of each mass after the collision.

Important Questions on Work, Power and Energy
A small block of mass moves on a frictionless surface of an inclined plane, as shown in the figure. The angle of the incline suddenly changes from to at point B. The block is initially at rest at A. Assume that collisions between the block and incline are totally inelastic. . The speed of the block at point immediately after it strikes the second incline is:
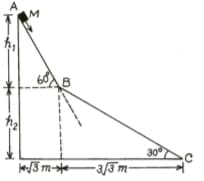
A small block of mass moves on a frictionless surface of an inclined plane, as shown in the figure. The angle of the incline suddenly changes from to at point B. The block is initially at rest at A. Assume that collisions between the block and incline are totally inelastic. . The speed of the block at point C, immediately before it leaves the second incline is:
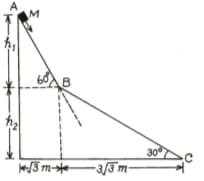
A small block of mass moves on a frictionless surface of an inclined plane, as shown in the figure. The angle of the incline suddenly changes from to at point B. The block is initially at rest at A. Assume that collisions between the block and incline are totally inelastic. . 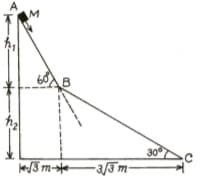
A particle moves along -axis from under a variable force . The work done in the process is:
The work done on a particle of mass by a force ( being a constant of appropriate dimensions), when the particle is taken from the point to the point along a circular path of radius about the origin in the plane is:
