MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
A ball collides perfectly inelastically with smooth horizontal ground at angle with vertical as shown. Fraction of kinetic energy lost by the ball due to collision is _____
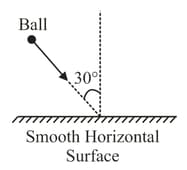

50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Work, Energy and Power
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
A rod of mass and length is lying on a horizontal table. The minimum work done in making it stand on one end will be _____.
(Take )
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
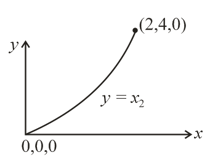
By applying a force a particle is moved along the path , where all quantities are in units, from point to the point . The work done by force on the particle (in joule), is _____.
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
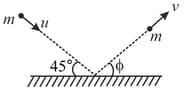
A particle of mass moving with a speed strikes a smooth horizontal surface at an angle . The particle rebounds at an angle with speed. If coefficient of restitution is , then angle is
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
