EASY
Earn 100
A ball of mass is dropped from a cliff of height . The ratio of its kinetic energy to the potential energy when it has fallen through a height is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
31.18% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Work, Energy and Power
MEDIUM
A body is moving unidirectionally under the influence of a source of constant power. The square of its displacement in time is proportional to
MEDIUM
If the potential energy between two molecules is given by then at equilibrium, separation between molecules, and the potential energy are:
MEDIUM
An asteroid of mass is approaching earth, initially at a distance with speed It hits Earth with a speed and are radius and mass of earth, then
EASY
If a spring of spring constant is compressed by , then the energy stored in the spring is
MEDIUM
A particle with total mechanical energy which is small and negative is under the influence of a one dimensional potential , where is in meters. At time , it is at . Then at a later time it can be found,
EASY
A block of mass moving at a speed of compresses a spring through a distance before its speed is halved. Find the spring constant of the spring
MEDIUM
A mass of moving with a speed of on a horizontal smooth surface, collides with a nearly weightless spring of force constant . The maximum compression of the spring would be
MEDIUM
A particle is released from a height . At a certain height its kinetic energy is half of its potential energy with reference to the surface of the earth. Height and speed of the particle at that instant are respectively
MEDIUM
A person trying to lose weight by burning fat lifts a mass of 10 kg upto a height of 1m 1000 times. Assume that the potential energy lost each time he lowers the mass is dissipated. How much fat will he use up considering the work done only when the weight is lifted up? Fat supplies J of energy per kg which is converted to mechanical energy with a 20% efficiency rate. Take :
MEDIUM
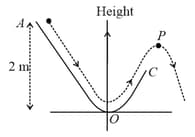
A particle slides down a frictionless track starting from rest at a point (height ). After reaching the particle continues to move freely in air as a projectile. When it reaches its highest point (height ), the kinetic energy of the particle (in ) is: (Figure drawn is schematic and not to scale; take ) ______________.
MEDIUM
The potential energy function for a two dimensional force is given by . The force that acts at the point is (Take and as unit vectors along - and - axes)
HARD
A particle is moving in a circle of radius under the action of a force which is directed towards centre of the circle. Total mechanical energy (kinetic energy + potential energy) of the particle is (take potential energy for ):
HARD
A mass of , initially at a height of above an uncompressed spring with spring constant is released from rest to fall on the spring. Taking the acceleration due to gravity as and neglecting the air resistance, the compression of the spring in is
MEDIUM
A uniform chain of mass and length is lying on a smooth horizontal table, with half of its length hanging down. The work done in pulling the entire chain up the table is
EASY
A body is released from a height of vertically downwards. The speed of the body at which potential energy is twice that of kinetic energy is (Acceleration due to gravity )
HARD
The potential energy of a diatomic molecule is a function dependent on (interatomic distance) as where, and are positive constants. The equilibrium distance between two atoms will be where ______ .
MEDIUM
The graphs below show the magnitude of the force on a particle as it moves along the positive -axis from the origin to . The force is parallel to the -axis and conservative. The maximum magnitude has the same value for all graphs. Rank the situations according to the change in the potential energy associated with the force, least (or most negative) to greatest (or most positive).

EASY
Hydrogen ion and singly ionized helium atom are accelerated, from rest, through the same potential difference. The ratio of final speeds of hydrogen and helium ions is close to:
HARD
Consider two masses with connected by a light inextensible string that passes over a pulley of radius and moment of inertia about its axis of rotation. The string does not slip on the pulley and the pulley turns without friction. The two masses are released from rest separated by a vertical distance When the two masses pass each other, the speed of the masses is proportional to
EASY
The potential energy of a system increases if work is done

