EASY
12th Tamil Nadu Board
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
A battery consists of a variable number () of identical cells, each having an internal resistance connected in series. The terminal of the battery is short-circuited. A graph of current versus the number of cells will be as shown in figure.
(a)
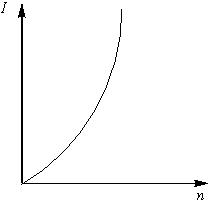

(b)
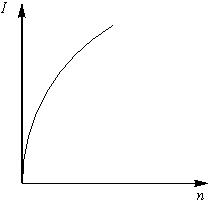

(c)
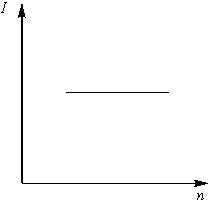

(d)
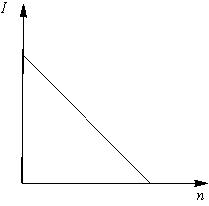

50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Current Electricity
EASY
12th Tamil Nadu Board
IMPORTANT
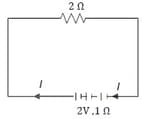
EASY
12th Tamil Nadu Board
IMPORTANT
EASY
12th Tamil Nadu Board
IMPORTANT
EASY
12th Tamil Nadu Board
IMPORTANT
HARD
12th Tamil Nadu Board
IMPORTANT
EASY
12th Tamil Nadu Board
IMPORTANT
HARD
12th Tamil Nadu Board
IMPORTANT
HARD
12th Tamil Nadu Board
IMPORTANT
