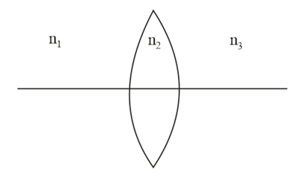
A biconvex lens of refractive index is placed such that the refractive index of the surrounding media is as shown. Then the lens


Important Questions on Ray Optics
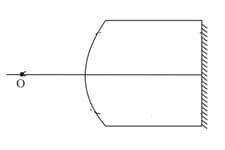
In the figure shown a point object is placed in the air on the principal axis. The radius of curvature of the spherical surface is . If is the final image formed after all the refractions and reflections.
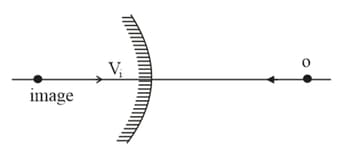
A particle is moving towards a fixed convex mirror. The image also moves. If speed of image and speed of the object, then
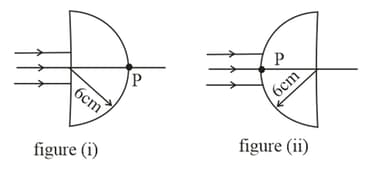
A parallel beam of light is incident normally on the flat surface of a hemisphere of radius and refractive index , placed in the air as shown in the figure . Assume paraxial ray approximation.
A ray is an incident on a refracting surface of refractive index at an angle of incidence and the corresponding angle of refraction is . The deviation of the ray after refraction is given by . Then, one may conclude that
A convex lens and concave lens are kept in contact and the combination is used for the formation of the image of a body by keeping it at different places on the principal axis. The image formed by this combination of lenses can be
A ray of light travelling in water is incident on its surface open to air. The angle of incidence is , which is less than the critical angle. Then, there will be
