MEDIUM
MHT-CET
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
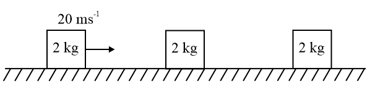
A block of mass collides with identical stationary block head on elastically with velocity of . After collision second block collides with the third block of mass initially at rest. If they collide head on perfectly inelastically then the velocity of their combination will be

(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Laws of Motion
EASY
MHT-CET
IMPORTANT
EASY
MHT-CET
IMPORTANT
EASY
MHT-CET
IMPORTANT
EASY
MHT-CET
IMPORTANT
EASY
MHT-CET
IMPORTANT
EASY
MHT-CET
IMPORTANT
EASY
MHT-CET
IMPORTANT
EASY
MHT-CET
IMPORTANT
