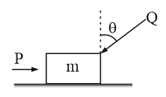
A block of mass , lying on a horizontal plane, is acted upon by a horizontal force and another force , inclined at an angle to the vertical. The block will remain in equilibrium if the coefficient of friction between it and the surface is (assume )


Important Questions on Newton's Laws of Motion (With Friction)
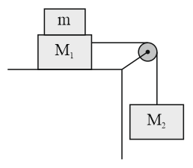
A solid block of mass is resting inside a cube as shown in figure. The cube is moving with a velocity . If the coefficient of friction between the surface of cube and block is , then the force of friction between the block and cube is
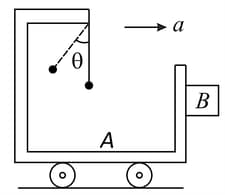
A trolley has a simple pendulum suspended from a frame fixed to its desk. A block is in contact on its vertical side. The trolley is on horizontal rails and accelerates towards the right such that the block is just prevented from falling. The value of coefficient of friction between and is . The inclination of the pendulum to the vertical is
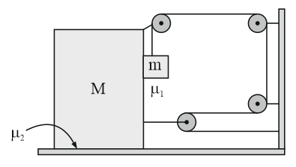
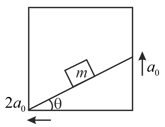
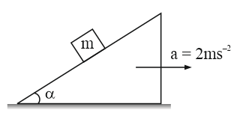
A block of mass is lying on a wedge having inclination angle . Wedge is moving with a constant acceleration . The minimum value of coefficient of friction so that remains stationary wedge is
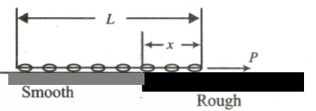
A chain of length is placed on a horizontal surface as shown in figure. At any instant is the length of chain on rough surface and the remaining portion lies on smooth surface. Initially . A horizontal force is applied to the chain (as shown in figure). In the duration, changes from to . For chain to move with constant speed,