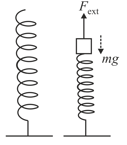
A block of mass is slowly lowered from a point where it just touches a vertical fixed spring of stiffness , till it remains stationary after the applied force is withdrawn. Find the work done by the external agent
in compressing the spring by a distance and
bringing the block to its stable equilibrium position.


Important Questions on Work, Energy and Power
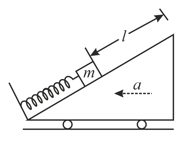
A block of mass is welded with a light spring of stiffness . The spring is initially relaxed. When the wedge fitted moves with acceleration , as shown in the figure, the block slides through a maximum distance relative to the wedge. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the wedge is , find the maximum deformation of the spring by using the work-energy theorem.
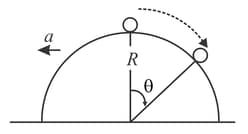
A small ball is placed at the top of a smooth hemispherical wedge of radius . If the wedge is accelerated with an acceleration , find the velocity of the ball relative to the wedge as the function of .
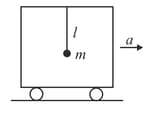
A pendulum of mass and length is suspended from the ceiling of a trolley which has a constant acceleration in the maximum deflection of the pendulum from the vertical. Find
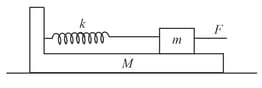
A constant force pushes the block till the wedge starts sliding. If the stiffness of the light spring connecting and is , coefficient of friction between block and wedge is , and between the wedge and ground is , then find the value of the force
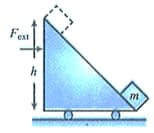
A block of mass is placed at the bottom of a massless smooth wedge which is placed on a horizontal surface. When we push the wedge with a constant force, the block move up the wedge. Find the work done by the external agent when the block has a speed and it reaches the top of the wedge.
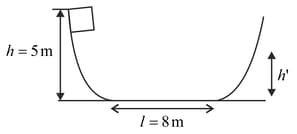
A block is released from rest from a height . After travelling through the smooth curved surface, it moves on the rough horizontal surface through a length and climbs onto the smooth curved surface through a height if , find