A body (object) is in equilibrium. State the resultant force on the body.

Important Questions on Turning Effects
A body (object) is in equilibrium. State the resultant turning effect on the body.
The figure shows a wheelbarrow with a heavy load of soil. Add an arrow to show how you could lift the left-hand end of the barrow with the smallest force possible. Remember to indicate clearly the direction of the force.
The figure shows a wheelbarrow with a heavy load of soil.
How do you know that the wheelbarrow is in equilibrium?
In the given diagram shows a beam balanced on a pivot. Add arrows to show the following forces:
A force pressing downwards on the beam that will have the greatest possible clockwise turning effect. Label this force .
A force pressing downwards on the beam that will have an anticlockwise turning effect equal in size to the turning effect of force . Label this force .
In the given diagram shows a beam balanced on a pivot. Add arrows to show the following forces:
A force pressing downwards on the beam that will have the greatest possible clockwise turning effect. Label this force .
A force pressing downwards on the beam that will have an anticlockwise turning effect equal in size to the turning effect of force . Label this force .
What other forces are acting, as well as the force , to keep the beam in equilibrium?
In the given diagram shows a beam balanced on a pivot. Add arrows to show the following forces:
A force pressing downwards on the beam that will have the greatest possible clockwise turning effect. Label this force .
A force pressing downwards on the beam that will have an anticlockwise turning effect equal in size to the turning effect of force . Label this force .
Why can we ignore these in calculating moments about the pivot?
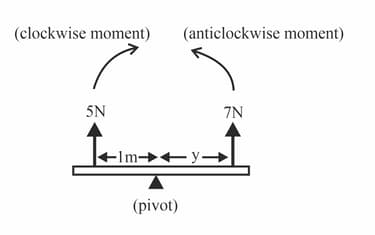
For the situations in figure, calculate the missing distance so that the beams are in equilibrium.
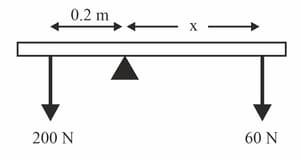
For the situations in the figure, calculate the missing distance so that the beams are in equilibrium.