EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
A body rotating with an angular speed of is uniformly accelerated to in The number of rotations made in the process is
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Kinematics
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
What will be the projection of vector on vector
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Three particles and are moving along the vectors and , respectively. They strike on a point and start to move in different directions. Now particle is moving normal to the plane which contains vector and Similarly particle is moving normal to the plane which contains vector and The angle between the direction of motion of and is Then the value of is
EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Match List I with List II.
| List I | List II | ||
| (a) | (i) | 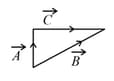 |
|
| (b) | (ii) | 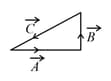 |
|
| (c) | (iii) | 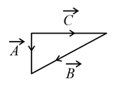 |
|
| (d) | (iv) | 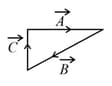 |
|
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
MEDIUM
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Water droplets are coming from an open tap at a particular rate. The spacing between a droplet observed at second after its fall to the next droplet is . At what rate the droplets are coming from the tap ? (Take )
HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
The relation between time and distance for a moving body is given as , where and are constants. The retardation of the motion is: (When stands for velocity)
HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
A balloon was moving upwards with a uniform velocity of . An object of finite mass is dropped from the balloon when it was at a height of from the ground level. The height of the balloon from the ground when object strikes the ground was around: (takes the value of as )
HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
The instantaneous velocity of a particle moving in a straight line is given as , where and are constants. The distance travelled by the particle between and is:
EASY
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Two vectors and have equal magnitude. The magnitude of is times the magnitude of . The angle between and is :
