A car of mass moving over a concave bridge of radius . Find the normal reaction acting on the car when it is at the lowest point of the bridge.

Important Questions on Circular Motion
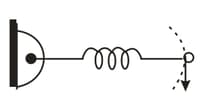
A particle of mass is moving with a constant speed in a circular path in a smooth horizontal plane (plane of the paper) by a spring force as shown in the figure. If the natural length of the spring is and the stiffness of the spring is , find the elongation of the spring.
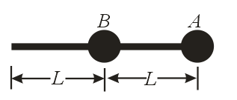
Ball A is attached to one end of a rigid massless rod, while an identical ball B is attached to the centre of the rod, as figure illustrates. Each ball has a mass and the length of each half of the rod is This arrangement is held by the empty end and is whirled around in a horizontal circle at a constant rate, so each ball is in uniform circular motion. Ball A travels at a constant speed of Find the tension in each half of the rod.
A bead of mass m slides along a curved wire lying on a horizontal surface as shown in figure.
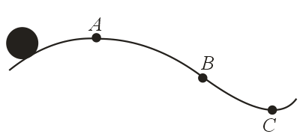
If the bead slides at constant speed along the wire, draw the vectors representing the force exerted by the wire on the bead at points .
Now consider the bead in figure speeds up with constant tangential acceleration as it moves towards the right. Draw the vectors representing the force on the bead at points .
(i) the tangential acceleration of the sphere,
(ii) the tension in the cord.
(iii) the magnitude of net force on the bob at the instant.
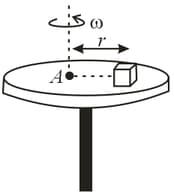
A small block is supported by a turn-table. The friction coefficient between block and surface is .
(a) If turn-table rotates at constant angular speed what can be the maximum angular speed for which the block does not slip?
(b) If the angular speed is increased uniformly from rest with an angular acceleration at what speed will the block slip?