A comet orbits the sun in a highly elliptical orbit. Does the comet have a constant linear speed, angular speed, angular momentum, kinetic energy, potential energy, total energy throughout its orbit? Neglect any mass loss of the comet when it comes very close to the Sun.
Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - Gravitation from NCERT PHYSICS PART 1 TEXTBOOK FOR CLASS XI Solutions
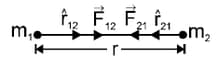
(i) Gravitational force acting between to bodies, where is the universal gravitational constant.
(ii) In vector form: &
2. Gravitational field:
(i) Gravitational field is related to the force as,
(ii) The field produced by a point mass is given by,
3. Variation of Acceleration due to Gravity:
(i) Acceleration due to gravity at height from the surface
(ii) Acceleration due to gravity at depth from the surface,
(iii) The equatorial radius is about longer than its polar radius. Hence
(iv) Acceleration due to gravity at latitude ,
4. Escape velocity:
It is the speed required from the surface of a planet to get out of the influence of the planet. For earth,
5. Satellite in a circular orbit:
(i) Satellite orbital Velocity,
(ii) Time period of satellite,
(iii) Potential energy of a Satellite: , Kinetic energy: and total energy
6. Kepler’s Laws:
(i) All planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one of the focal points
(ii) The line joining the sun and a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time.
(iii) The square of the orbital period of a planet is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the elliptical orbit of the planet. The time period and radius of the circular orbit of a planet about the sun are related as
