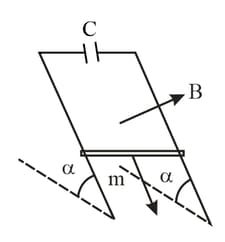
A copper connector of mass slides down two smooth copper bars, set at an angle to the horizontal, due to gravity. At the top, the bars are interconnected through a capacitor, of capacitance . The separation between the bars is equal to . The system is located in a uniform magnetic field of induction , perpendicular to the plane in which the connector slides. The resistances of the bars, the connector and the sliding contacts as well as the self-inductance of the loop, are assumed to be negligible. Find the acceleration of the connector.


Important Questions on ELECTRODYNAMICS
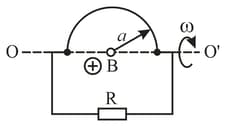
A wire shaped as a semi-circle of radius , rotates about an axis with an angular velocity , in a uniform magnetic field of induction . The rotation axis is perpendicular to the field direction. The total resistance of the circuit is equal to . Neglecting the magnetic field of the induced current, find the mean amount of thermal power being generated in the loop during a rotation period.
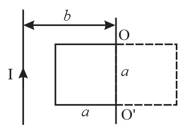
A square wire frame with side and a straight conductor carrying a constant current are located in the same plane . The inductance and the resistance of the frame are equal to and respectively. The frame was turned through about the axis separated from the current-carrying conductor by a distance . Find the electric charge having flown through the frame.
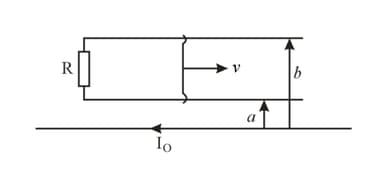
A long straight wire carries a current, . At distances and from it there are two other wires, parallel to the former one, which are interconnected by a resistance, . A connector slides without friction, along the wires, with a constant velocity, . Assuming the resistances of the wires, the connector, the sliding contacts and the self-inductance of the frame to be negligible, find,
the magnitude and the direction of the current induced in the connector;
the force required to maintain the connector's velocity constant.
A conducting rod , of mass , slides without friction over two long conducting rails, separated by a distance . At the left end, the rails are interconnected by a resistance . The system is located in a uniform magnetic field, perpendicular to the plane of the loop. At the moment , the rod starts moving to the right with an initial velocity . Neglecting the resistances of the rails and the rod , as well as the self-inductance, find,
the distance covered by the rod until it comes to a standstill,
the amount of heat generated in the resistance during this process.
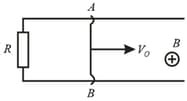
A connector can slide, without friction, along a -shaped conductor, located in a horizontal plane. The connector has a length , mass and resistance . The whole system is located in a uniform magnetic field of induction , directed vertically. At the moment , a constant horizontal force starts acting on the connector, shifting it translation-wise, to the right. Find how the velocity of the connector varies with time . The inductance of the loop and the resistance of the -shaped conductor are assumed to be negligible.
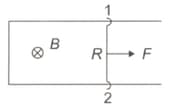
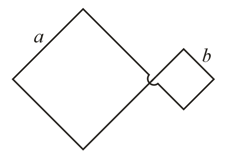
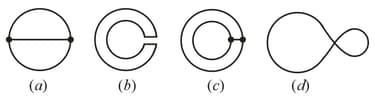
Figure illustrates plane figures made of thin conductors which are located in a uniform magnetic field, directed away from a reader, beyond the plane of the drawing. The magnetic induction starts diminishing. Find how the currents induced in these loops are directed.
A plane loop shown in the figure is shaped as two squares with sides, and , and is introduced into a uniform magnetic field at right angles to the loop's plane. The magnetic induction varies with time as , where and . Find the amplitude of the current induced in the loop, if its resistance per unit length is equal to . The inductance of the loop is to be neglected.