A crate is sliding down a slope. The weight of the crate is . The slope makes an angle of With the horizontal. Draw a diagram to show the situation. Include arrows to represent the weight of the crate and the contact force of the slope acting on the crate.

Important Questions on Forces: Vectors and Moments
A crate is sliding down a slope. The weight of the crate is . The slope makes an angle of With the horizontal. Calculate the component of the weight down the slope.
A crate is sliding down a slope. The weight of the crate is . The slope makes an angle of with the horizontal. Explain why the contact force of the slope has no component down the slope.
A crate is sliding down a slope. The weight of the crate is . The slope makes an angle of with the horizontal. What third force might act to oppose the motion? In which direction would it act.
A child of mass is on a water slide. The slide slopes down at to the horizontal. The acceleration of free fall is . Calculate the child's acceleration down the slope: when there is no friction and the only force acting on the child is his weight
A child of mass is on a water slide. The slide slopes down at to the horizontal. The acceleration of free fall is . Calculate the child's acceleration down the slope: If a frictional force of acts up the slope.
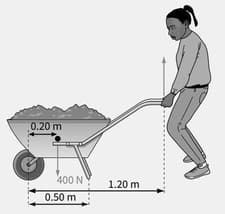
A wheelbarrow is loaded as shown in Figure.
Calculate the force that the person needs to exert to hold the wheelbarrow's legs off the ground.
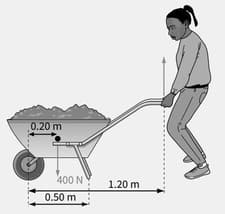
A wheelbarrow is loaded as shown in Figure.
Calculate the force exerted by the ground on the legs of the wheelbarrow (taken both together) when the gardener is not holding the handles.
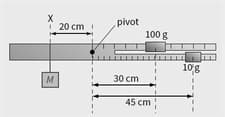
A traditional pair of scales uses sliding masses of and To achieve a balance. A diagram of the arrangement is shown in Figure. The bar itself is supported with its centre of gravity at the pivot. Calculate the value of the mass , attached at .